Angiosperms
400 likes | 768 Vues
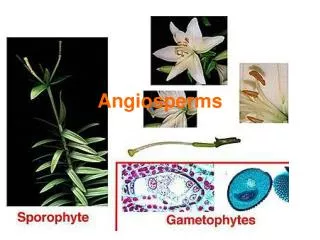
Angiosperms. Group 3: Seed producing, Vascular Plants. Type 2: Angiosperms (flowering plants) Flower = reproductive structure Attract animals to help spread pollen Forms fruit to protect and spread seeds Seeds Grow inside the fruit Inside the seed 1. Embryo 2. Food supply.

Angiosperms
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Group 3: Seed producing, Vascular Plants Type 2: Angiosperms (flowering plants) Flower = reproductive structure Attract animals to help spread pollen Forms fruit to protect and spread seeds Seeds Grow inside the fruit Inside the seed 1. Embryo 2. Food supply
Seed Dispersal • Fruit brightly colored • Attracts animals • Seeds pass through animals digestive system • Seeds pooped in a new area to grow Fruit seeds in fox poop
Angiosperm Groups • 2 groups: Monocots and Dicots (based on seed type) • Cotyledon: embryonic leaf • Two Categories: • Monocots: embryo with 1 seed leaf • Dicots: embryo with 2 seed leaves
Monocots vs. Dicots Easy to see Easy to see
Apple Tree: Monocot or Dicot? 2 3 1 Net-like veins 4 5
Monocot or Dicot? 2 3 1 4 6 5
Monocot or Dicot? Veins run parallel
Monocot or Dicot? Veins run parallel
Monocot or Dicot? Veins branch outward
Angiosperm Life Spans Seed grows in 2011 Seed grows in 2010 Plant dies in winter 2010…but seeds will grow in 2011 Plant dies in winter 2011 Plant grows during the spring & summer of 2011 Plant grows during the spring & summer of 2010 Flower grows during autumn of 2010 Flower grows during autumn of 2011 • Three Life Span Types: 1. Annuals • 1 year: Seed grows…produce flowers & seeds…die
Angiosperm Life Spans Seed grows in 2010 Plant dies in winter of 2011…but seeds grow next year Plants grows during spring & summer of 2010 Flower & seeds created during autumn of 2011 Plant goes dormant during winter of 2010 Plant grows during spring & summer of 2011 • Three Life Span Types: 2. Biennials • 1st year: Seed grows and stores food • 2nd year: grows more, makes flowers & seeds…dies
Angiosperm Life Spans Seed grows in 2010 Plant grows during spring & summer of 2010 Plant grows during spring & summer of 2011 Plant grows during spring & summer of 2012 Plant grows during spring & summer of 2013 Plant dies in winter of 2013 Plant goes dormant during winter of 2010 Plant goes dormant during winter of 2011 Plant goes dormant during winter of 2012 Plant goes dormant during winter of 2013 Flower & seed grows during autumn of 2011 Flower & seed grows during autumn of 2012 Flower & seed grows during autumn of 2013 Flower & seed grows during autumn of 2010 • Three Life Span Types: 3. Perennials • Live for more than 2 years
Flowers petals sepals • Reproductive structure of flowering plants • Sepals • outer ring of leaves • protection • Petals • Inner ring of leaves • Brightly colored to attract pollinators • Open petals & sepals reveal male and female structures
Tulip Pistil and Stamen female male
Lily Pistil and Stamen female male
Pistil and Stamen female male
Pistil and Stamen female male
Flowers • Female Carpel • Inner most part • Ovary: within the base • Female gametophyte • Becomes the fruit when fertilized • Stigma: sticky tip, collects pollen • Male Stamen • Anther: produces pollen • Pollen: male gametophyte
Cross-Pollination(pollen of one, fertilizes egg of another) . . .
Pollen transferred to the stigma…. Pollen tube grows towards the egg…. Pollen nucleus travels down pollen tube to fertilize the egg . egg zygote
Flower petals start to fall off and dies…. Fruit develops zygote
Animals eat fruit….seeds come out the other end…cycle repeats seed
HW: Bring a flower to school. One with distinct male and female parts.
Tulip Pistil and Stamen female male
Lily Pistil and Stamen female male
Pistil and Stamen female male
Pistil and Stamen female male
Kobe Kuiz • What is the reproductive structure of angiosperms called? • What structure protects the seeds of angiosperms? • Why are flowers and fruits often brightly colored? • Be able to identify the parts of a flower diagram. • Which flower part produces pollen? • Which flower part will pollen land upon? • Which flowers only live for 2 years and then die? • Practice the monocot/dicot sample questions.