Tissues
190 likes | 210 Vues
This article provides an overview of tissues, including their types, functions, and characteristics. It explains the different types of epithelial tissue and their specific functions, as well as the structure and properties of glandular epithelium. The article also discusses the types of secretion in exocrine glands and the methods of secretion.

Tissues
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Tissues A group of cells that work together
2 main parts to tissues • Living- cells • Nonliving- noncellular -intracellular space called matrix
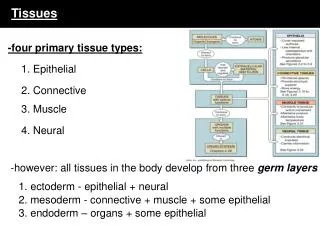
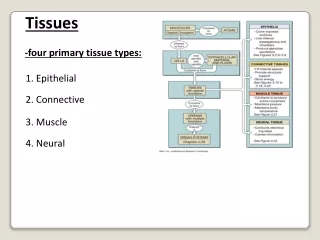
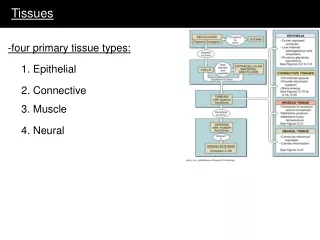
Types of tissues • Epithelium • Connective • Muscle • Nervous
Epithelial Tissue Functions • Protection • Control Permeability/absorption • Secretion • Surface Transportation • Sensation
Epithelial characteristics • Cells are packed and held together with desmosomes • Cells are attached to basement membrane • Basement membrane and ET are avascular!!
Cell arrangement • Single layer, called SIMPLE • Many layers, called STRATIFIED • Looks layered but really just a single layer, called PSEUDOSTRATIFIED
Cell Shapes • Based on OUTER LAYER ONLY!!! • Flat= squamous • Rounded= cuboidal • Tall= columnar
Simple Squamous • “fried egg” shape • Found lining tubules and capillaries
Simple Cuboidal • Found in ducts of glands, in ovaries, and capsule surrounding lens of eye
Simple Columnar • Often specialized for protection, secretion or absorption • May contain goblet cells which produce mucus • May contain cilia – in respiratory tract, uterine tubes • May contain microvilli – appears as “brush border”, found in small intestine and kidney tubules
Stratified Squamous • Function in protection from “mechanical stress” • Found in skin, oral cavity, esophagus, and vagina • May be keratinized(skin) or not(inside of mouth, vagina)
Found in ducts of sweat gland of skin Stratified Cuboidal
Stratified Columnar • Functions in protection and secretion • Found in urethra
Pseudostratified Columnar • Staggered nuclei give appearance of more than 1 layer • Often contain goblet cells • Ciliated( respiratory tract and middle ear) and nonciliated (in urethra and parotid gland)
Surface cells may be binucleate Cells are loosely packed which gives elasticity Found in bladder, ureters and kidneys Transitional
Glandular epithelium • Function in secretion • EXOCRINE- secrete product into a duct system or onto a free surface ex- enzymes, sweat, milk, sweat 2. ENDOCRINE- secrete a product directly into bloodstream ex.- hormones
Exocrine Gland • Size- a. Unicellular- ex. Goblet cell b. Multicellular • Shape a. Tubular, acinar/alveolar, tubuloalveolar • Type of Secretion- a. Serous- watery w/ enzymes b. Mucous c. mixed
4. Method of secretion a. Merocrine- expel only secretion by exocytosis - ex. sweat, salivia, mucus b. Aprocrine- release portion of cell with secretory product - ex. mammary glands, underarm sweat c. Holocrine- a whole cell is secretory product - ex. Sebaceous or oil glands, testes and ovaries