Real Roots and Rational Exponents
80 likes | 102 Vues
This text provides examples and solutions for finding real roots of numbers, evaluating expressions with rational exponents, and approximating roots using a calculator.

Real Roots and Rational Exponents
E N D
Presentation Transcript
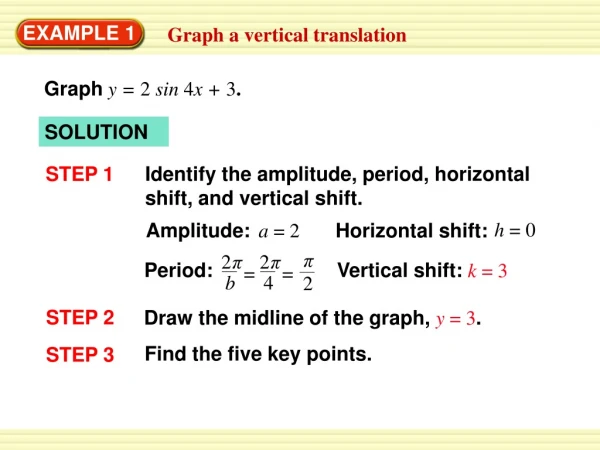
a. Because n = 3 is odd and a = –216 < 0, –216 has one real cube root. Because (–6)3= –216, you can write = 3√–216 = –6 or (–216)1/3 = –6. b. Because n = 4 is even and a = 81 > 0, 81 has two real fourth roots. Because 34 = 81 and (–3)4 = 81, you can write ±4√ 81 =±3 EXAMPLE 1 Find nth roots Find the indicated real nth root(s) of a. a. n = 3, a = –216 b. n = 4, a = 81 SOLUTION
1 1 23 323/5 64 ( )3 = (161/2)3 = 43 = 43 = 64 = = 16 1 1 1 1 1 1 = = = = ( )3 (321/5)3 323/5 32 5 8 23 8 = = = = EXAMPLE 2 Evaluate expressions with rational exponents Evaluate (a) 163/2 and (b)32–3/5. SOLUTION Radical Form Rational Exponent Form a. 163/2 163/2 b. 32–3/5 32–3/5
Keystrokes Expression Display 9 1 5 7 3 4 12 3 8 7 c. ( 4 )3 = 73/4 EXAMPLE 3 Approximate roots with a calculator a. 91/5 1.551845574 b. 123/8 2.539176951 4.303517071
Because n = 4 is even and a = 625 > 0, 625 has two real nth roots. Because 54= 625 and (–5)4= 625, you can write 4√ 625 = ±5 or ±(625)1/4 = ±5. Because n = 6 is even and a = 64 > 0, 64 has two real nth roots. Because 26= 64 and(–2)6= 64, you can write 6√ 64= ±2 or ±(64)1/6 = ±2. for Examples 1, 2 and 3 GUIDED PRACTICE Find the indicated real nth root(s) of a. 1. n = 4, a = 625 SOLUTION 2.n = 6, a = 64 SOLUTION
Because n = 3 is odd and a = –64 < 0, –64 has one real cube root. Because (–4)3= –64, you can write 3√–64= –4 or (–64)1/3 = –4. Because n = 5 is odd and a = 243 > 0, 243 has one real nth root. Because (3)5= 243, you can write 5√243 = 3 or (243)1/5 = 3. for Examples 1, 2 and 3 GUIDED PRACTICE Find the indicated real nth root(s) of a. 3. n = 3, a = –64. SOLUTION 4. n = 5, a = 243 SOLUTION
1 3 = for Examples 1, 2 and 3 GUIDED PRACTICE Evaluate expressions without using a calculator. 5. 45/2 SOLUTION 45/2 = (41/2)5 = 25 = 32 6. 9–1/2 SOLUTION 9–1/2 = (91/2)–1 = 3–1
for Examples 1, 2 and 3 GUIDED PRACTICE Evaluate expressions without using a calculator. 7. 813/4 SOLUTION 813/4 = (811/4)3 = 33 = 27 8. 17/8 SOLUTION 17/8 = (11/8)7 = (1)7 = 1
Keystrokes Expression Display 4 2 5 1 64 - 2 3 10. 64 2/3 – 11. (4√ 16)5 –30 2 3 12. (3√–30)2 16 5 4 for Examples 1, 2 and 3 GUIDED PRACTICE Evaluate the expression using a calculator. Round the result to two decimal places when appropriate. 9. 42/5 1.74 0.06 32 9.65