Group 7 Elements
410 likes | 1.37k Vues
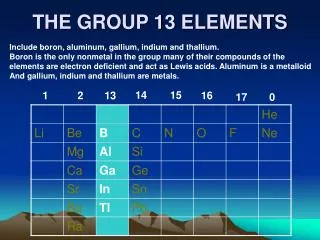
Group 7 Elements. By Yazan Dabbagh. Introduction. Group 7 elements are commonly referred to as halogens. There are five elements and they include f luorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine and astatine. Properties. They don’t conduct electricity and have low melting and boiling points.

Group 7 Elements
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Group 7 Elements By Yazan Dabbagh
Introduction • Group 7 elements are commonly referred to as halogens. • There are five elements and they include fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine and astatine
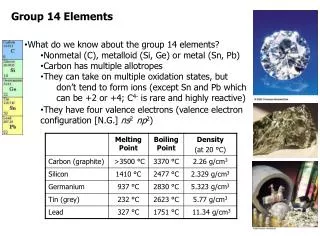
Properties • They don’t conduct electricity and have low melting and boiling points. • They are diatomic molecules and are reactive non-metals • All of them have 7 outer shell electrons . • At room temperature fluorine and chlorine are gases, bromine is a liquid and iodine and astatine are solids • Their colors get darker as we go down the group (fluorine is colorless- astatine is black) • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=u2ogMUDBaf4
Fluorine Fluorine is a poisonous halogen, it is colorless and it is the most chemically reactive and electronegative of all the elements. It is so reactive that glass, metals, and even water, as well as other substances, burn with a bright flame in a jet of fluorine gas. Fluorine is essential for the maintenance of solidity of our bones. Fluorine can also protect us from dental decay, if it is applied through toothpaste twice a day. If fluorine is absorbed too frequently, it can cause teeth decay, osteoporosis and harm to kidneys, bones, nerves and muscles.
Chlorine The pure chemical element has the physical form of a diatomic green gas. The name chlorine is derived from the Latin word chloros, meaning green, referring to the color of the gas. Chlorine gas is two and one half times as heavy as air, has an intensely disagreeable suffocating odor, and is exceedingly poisonous. In its liquid and solid form it is a powerful oxidizing, bleaching, and disinfecting agent. Chlorine is an important chemical in water purification, in disinfectants, in bleach and in mustard gas. Chlorine is also used widely in the manufacture of many products and items directly or indirectly, i.e. in paper product production, antiseptic, dyestuffs, food, insecticides, paints, petroleum products, plastics, medicines, textiles, solvents, and many other consumer products. It is used to kill bacteria and other microbes from drinking water supplies.
Bromine At room temperature bromine is a brownish-red liquid. It has a similarly colored vapor with an offensive and suffocating odor. It is the only nonmetallic element that is liquid under ordinary conditions, it evaporates easily at standard temperature and pressures in a red vapor that has a strong disagreeable odor resembling that of chlorine. Bromine is less active chemically than chlorine and fluorine but is more active than iodine; its compounds are similar to those of the other halogens. Bromine is soluble in organic solvents and in water. Bromine is used in making fumigants, dyes, flame proofing agents, water purification compounds, sanitizes, medicinal, agents for photography and in brominates vegetable oil, used as emulsifier in many citrus-flavored soft drinks.
Iodine Iodine is a non-metallic, dark-gray/purple-black, lustrous, solid element. Iodine is the most electropositive halogen and the least reactive of the halogens even if it can still form compounds with many elements. Iodine sublime easily on heating to give a purple vapor. Iodine dissolves in some solvents, such as carbon tetrachloride and it is only slightly soluble in water. Iodine is used in medical treatment, it is employed in the preparation of certain drugs and in the manufacture of some printing inks and dyes. Silver iodine is used in photography. Iodine is added to almost all the table salt and is used as a supplement to animal feed. It is also an ingredient of water purification tablets that are used for drinking water preparation.
Astatine Astatine is a highly radioactive element and it is the heaviest known halogen. Its chemical properties are believed to be similar to those of iodine. Is has been little researched because all its isotopes have short half lives. All that is known about the element has been estimated from knowing its position in the periodic table below iodine and by studying its chemistry in extreme diluted solutions. Astatine is never encountered outside nuclear facilities or research laboratories. Total world production of astatine to date is estimated to be less than a millionth of a gram, and virtually all of this has now decayed away.
Fun Facts and video They require one more electron to fill their outer electron shells, therefore are highly reactive, and as such can be harmful or lethal to biological organisms in sufficient quantities. Fluorine is the most reactive element in existence, even attacking glass, and forming compounds with the heavier noble gases. Halogen reactions produce salts known as halides. There is another halogen called Ununseptium which hasn't been discovered yet.