Enhancing Resource Productivity and Future Technologies for Sustainable Development
150 likes | 271 Vues
The conference, held in Copenhagen on November 18-19, 2010, focuses on resource productivity, final sink scarcity, and future technologies. It emphasizes metrics essential for evaluating resource efficiency within Europe. Key speakers from the Charles University Environment Center discuss the coupling of physical and financial flows, the rebound effect of increased efficiency, and the impacts of consumption-driven economic growth. Technologies highlighted include energy-efficient buildings, renewable energy solutions like solar and wind, and advancements in transportation, promoting sustainable practices for a better future.

Enhancing Resource Productivity and Future Technologies for Sustainable Development
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Resource productivity and future technologies Miroslav Havránek EEA - FLIS - COPENHAGEN - 18.-19. 11.2010
Content • About CUEC • Resource productivity • Final sink scarcity • Future technologies • ISIE ConAccount news
Charles University Environment Center • Charles University in Prague • Non-faculty research institute (1992) • About 30 people (director prof. Bedrich Moldan) • Focus on environmental and ecological economy, sustainable development indicators
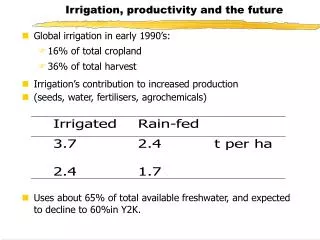
Resource productivity metrics • EEA Core set • EUROSTAT • IEA • Upstream processes omitted • Rucksack, Footprinting, Hybrid I-O tables
Resource productivity in Europe Source: EUROSTAT
Energy intensity per product Source: CZSO
Increasing efficiency - pitfall • Physical and financial flows are coupled • Resource efficiency leads to higher quality of life and ultimatelly to more resource use = rebound effect is real • Economic growth is driven by consumption (income) • To effectively de-couple and decrease env. burden efficiency must grow faster than GDP
Final sink • Resource becomes waste • Dematerialisation shifts materials to more dangerous materials • Recycling vs. Final disposal • Air & Soil & Sea
Technology development • Strong driver of the future • Omitted environmental impacts and resource needs • Non-linearities in future scenarios • Penetration curve of new technologies • Know-how exchange
Accelerating technologies: race in to unknown? • Improvement of technology vs. Change of basic principles
Technology outlook of LDV, IEA Source: IEA 2010
Technologies example:Demand Side • Energy efficiency in buildings and appliances • Heat pumps • Solar space and water heating • Energy efficiency in transport • Electric and plug-in vehicles • H2 fuel cell vehicles • CCS industry, H2 and fuel transformation • Industrial motor systems
Technologies example:Suply side • CCS fossil-fuel power generation • Nuclear power plants • Onshore and offshore wind • Biomass IGCC & co-combustion • Photovoltaic systems • Concentrating solar power • Coal: integrated-gasification combinedCycle • Coal: ultra-supercritical • 2nd generation biofuels