Relative Pronouns
160 likes | 553 Vues
Relative Pronouns. Forms. Qui, Quae, Quod, Qui, Quae, Quae, Cuius, Cuius, Cuius Quorum, Quarum, Quorum First there’s Cui and then there’s Quibus Quem, Quam, Quod and Quos, Quas, Quae Quo, Qua, Quo and then there’s Quibus Now we’re done. Forms – The Relative Pronoun Song.

Relative Pronouns
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Qui, Quae, Quod, Qui, Quae, Quae, Cuius, Cuius, Cuius Quorum, Quarum, Quorum First there’s Cui and then there’s Quibus Quem, Quam, Quod and Quos, Quas, Quae Quo, Qua, Quo and then there’s Quibus Now we’re done Forms – The Relative Pronoun Song
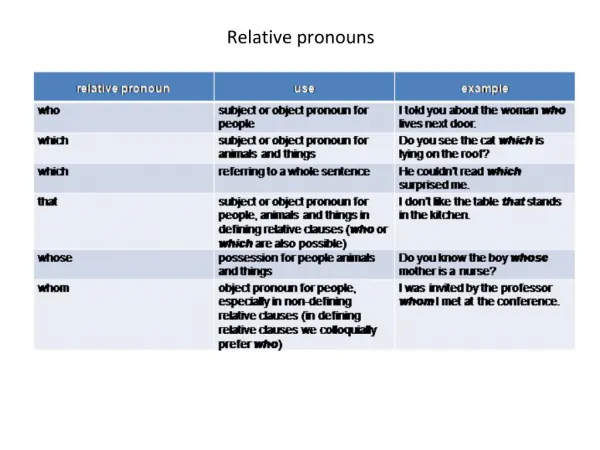
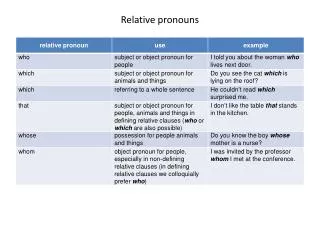
Relative Pronouns • Words that introduce a relative clause: • Who • Which • What • That • Whose • To whom • By Whom, etc.
Relative Pronoun Use • Used in a relative clause • A relative clause is always a dependent clause • You can remove the relative clause and still have a complete sentence. • A relative clause acts as an adjective – it describes a noun or noun substitute in the main sentence. We call this an adjectival clause. • The noun the clause modifies is called the antecedent. • Example: The boy who lived in the house is good.
Relative Pronoun Use • Example: The boy who lived in the house is good. • Let’s look more closely: • Who lived in the house is a dependent clause. • Who lived in the house describes boy. • Who lived in the house begins with a relative pronoun. • Who lived in the house is a relative clause. • What is the antecedent?
Nunc, Latina The relative pronoun agreement is not quite like an adjective agreement: - The relative pronoun agrees with the antecedent in gender and number. - The relative pronoun takes it’s case from the clause in which it is used.
Nunc, Latine • Puer qui in casa habitavit est bonus. The relative pronoun agrees with the antecedent in gender and number. - Puer is the antecedent, so the relative pronoun is masculine and singular. The relative pronoun takes its case from the clause in which it is used. Who is the subject of the clause, so the relative pronoun is nominative.
Qui, Quae, Quod, Qui, Quae, Quae, Cuius, Cuius, Cuius Quorum, Quarum, Quorum First there’s Cui and then there’s Quibus Quem, Quam, Quod and Quos, Quas, Quae Quo, Qua, Quo and then there’s Quibus Now we’re done Let’s Sing Again!