Animal Evolution
330 likes | 567 Vues
Animal Evolution. But first….some review!. 0 of 16. Unlike plants, animals have…. Cell membranes Histone proteins Cell walls Centrioles Glucose molecules. The organism to the right belongs to the phylum:. Reptilia Mammalia Amphibia Chordata Arthropoda. 0 of 16. 0 of 16.

Animal Evolution
E N D
Presentation Transcript
0 of 16 Unlike plants, animals have… • Cell membranes • Histone proteins • Cell walls • Centrioles • Glucose molecules
The organism to the right belongs to the phylum: • Reptilia • Mammalia • Amphibia • Chordata • Arthropoda 0 of 16
0 of 16 The principal components of viruses are: • Protein and lipid • DNA and RNA • RNA and lipid • DNA and carbohydrate • protein and nucleic acid
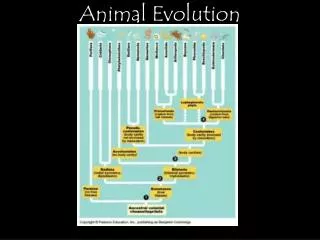
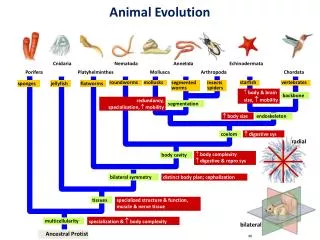
Animal Evolution • Monophyletic • Common ancestor • Colonial Flagellate Hypothesis • All animals descended from a colony of hollow spherical cells
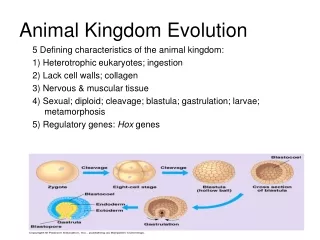
Animal Classification • Tissue organization • May be made of cells, tissues or organs • 3 GERM LAYERS • Endoderm • Mesoderm • Ectoderm • DIPLOBLASTIC • just endo & ectoderm; have tissues only (no organs) • TRIPLOBLASTIC • all three; have organs
Animal Classification • Symmetry • Asymmetrical • Symmetrical • Cephalization
Animal Classification • Body Plan • “Sac plan” • One opening for food to enter and exit • “Tube w/in a tube” • Mouth and anus • Allows for specialization along digestive tract
Animal Classification • Type of Coelom • Acoelomates • No body cavity or coelum (tube) • Psuedocoelomates • Body cavity incompletely lined by mesoderm • Coelomates • Body cavity completely lined by mesoderm
Animal Classification PROTOSOMES DEUTEROSOMES First embryonic opening becomes the anus • First embryonic opening (blastopore) becomes the mouth of the organism
Animal Classification • Segmentation Evolutionary Advantage of Segmentation?
And finally… • Molecular Data • Closely related organisms should have a similar nucleotide sequence
Tissues • 4 types • EPITHELIAL • CONNECTIVE • MUSCULAR • NERVOUS
Epithelial Tissue • Protective layer of cell that lines body cavities • Specialized to: • Secrete • Absorb • Excrete • filter
Types of Epithelial Tissue • SIMPLE – one layer • STRATIFIED - more than one layer • BASEMENT MEMBRANE – bottom
Connective Tissue • Many shapes and sizes, but all have: • Specialized cells • Ground substance • Non-cellular “stuff” that separates the cells • Solid, liquid or gel • Protein fibers
Connective Tissue • 4 types • Fibrous • Loose • Adipose • Dense • Supportive • Cartilage • Bone • Fluid • Blood • Lymph
Muscle • Cells with actin and myosin filaments that allow for movement • 3 types • SKELETAL • SMOOTH • CARDIAC
Nervous Tissue • Functions in sensing, interpreting, and responding to stimuli • NEURON • NEUROGLIAL CELL – support and nourishes neurons
The Skin as an Organ • How is the skin adapted in each of the following organisms?
Skin as an Organ • Skin has many layers • Epidermis • Outer protective layer • Dermis • Contains receptors and blood supply • Subcutaneous • Fat layer • Blood supply
Body Cavities • Various body cavities contain different organs • Ventral (“belly”) cavity of human develops from coelom
Homeostasis • Give an example of how each system helps the body maintain homeostasis. Respiratory Digestive Cardiovascular Circulatory Skeletal Muscular
Negative Feedback • Sensor becomes active when a change is detected • Signals control center which then fixes the problem • Examples?
Positive Feedback • Stimulus causes a greater change in the same direction • Example: • Pressure of the baby’s head pushes on cervix • Stimulates release of oxcytocin • Oxcytocin stimulates contraction of uterus and more pressure
Critiquing a research paper which form of feedback? • Negative • Positive
Which of the following best describes the set point of a homeostatic system? • The cells that collect and transmit information about the state of the system. • The cells that receive information about the state of the system and that direct changes to the system. • The various components that produce appropriate changes in the system. • The target or “normal” value of the parameter in question. 0 of 30