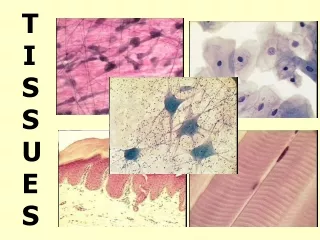
TISSUES
790 likes | 810 Vues
TISSUES. I. Introduction. Basics Tissues Group of cells with similar structure and function 2. The study of tissues = Histology. I. Introduction. Basics 3.Tissues consist of two components a) cells b) extracellular matrix of water small solutes

TISSUES
E N D
Presentation Transcript
I. Introduction • Basics • Tissues Group of cells with similar structure and function 2. The study of tissues = Histology
I. Introduction • Basics 3.Tissuesconsist of two components a) cells b) extracellular matrix of • water • small solutes • fibrous proteins
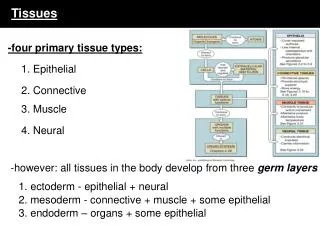
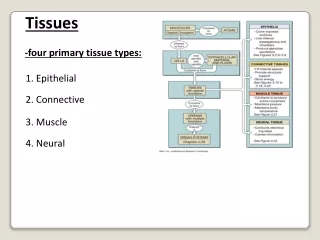
I. Introduction • There are 4 tissue types 1. Epithelial tissue protection 2. Connective tissue support 3. Muscle tissue movement 4. Neural tissue control
II. Epithelial Tissue • A. Location • includes outer layer of skin • lines the tubes and open cavities of the digestive and respiratory systems • lines blood vessels & heart
II. Epithelial Tissue • A. Location • covers walls & organs of ventral body cavity • forms glands & sense organs
II. Epithelial Tissue B. Functions 1. Protects from mechanical & chemical injury 2. Protects against bacterial invasion 3. Filters, absorbs, secretes
II. Epithelial Tissue • C. Description • tightly packed cells • little or not visible matrix • may have singular or multiple layers
C. Description • has a free surface • is firmly attatched to a basement membrane • 6. can divide rapidly (regeneration)
C. Description • is avascular • receive nutrients by diffusion
D. Classification 1. Number of cell layers a. Simple • single layer of cells • each cell extends from the basement membrane to the free surface. • Function • absorption, secretion, filtration
D. Classification 1. Number of cell layers • b. Stratified • more than one layer of cells • only one layer is adjacent to the basement membrane. • high stress areas
D. Classification 1. Number of cell layers c. Pseudostratified • 1 layer of cells • Each cell touches basement membrane • Appears stratified
II. Epithelium D. Classification 1. Number of cells 2. Cell Shape • a. Squamous • Squashed, scale like • Flat nucleus
2. Cell Shape b. Cuboidal • Squarish or hexagonal in profile • Nucleus round & centrally located
D. Classification 1. Layers • Cell Shape a. Squamous b. Cuboidal c. Columnar • longer than wide • cylindrical • nucleus near basement membrane
D. Classification 2. Cell Shape d. Transitional • combination of shapes • tolerates stretching
II. Epithelial Tissue E. Endothelium 1. Covers and lines a) heart b) blood vessels 2. Simple squamous • slick & thin • capillaries are permeable
II. Epithelial Tissue F. Epithelial Membranes 1. Epithelium + connective tissue = small organs 2. Mucosae membranes • Line organs, body cavities • Open to exterior • Respiratory, digestive urogenital
F. Epithelial Membranes 2. Mucosae membranes • Lining of mouth = stratified squamous • Lg & Sm Intestine = columnar
F. Epithelial Membranes 3. Serosa • Lines ventral, visceral, parietal cavities walls of air sacs in lungs = simple squamous
F. Epithelial Membranes 3. Synovial • Lines joints • cushions, protects
G. Cutaneous Epithelium 1. Is the skin • Keratinized, dry epidermis 2. Epidermis is stratified squamous
II. Epithelium H. Glandular Epithelium 1. Characteristics a) cells specialized to produce and secrete substances b) cells typically columnar or cuboidal c) Kinds: Endocrine & Exocrine
H. Glandular Epithelium 2. Endocrine: a) produce hormones which regulate or coordinate other cells
H. Glandular Epithelium 2. Endocrine: b) ductless: release secretions into the blood
H. Glandular Epithelium 2. Endocrine: c) Examples: thyroid, pituitary, adrenal
THYROID GLAND LUMEN
H. Glandular Epithelium 3. Exocrine: a) release secretions into the ducts b) Examples: salivary, mammary, sweat, oil
E. Glandular Epithelium 3. Exocrine: c) Structure simple - unbranched compound – branched
E. Glandular Epithelium 3. Exocrine: c) Structure tubular – uniform diameter
E. Glandular Epithelium 3. Exocrine: c) Structure acinar – secretory cells in sac at end
E. Glandular Epithelium 3. Exocrine: c) Structure tubuloacinar – secretory cells in both sac and tube
Connective TissueThe most abundant tissue • A. Functions • bind structures together • (tendons) • provide support • (bones) • protection • (cartilage • insulation • (fat) • transportation • ) (blood)
III. Connective Tissue • B. Description • cells scattered among fibers and matrix • intercellular material • Vascular to avascular • Cells capable of division
III. Connective Tissue • C. Kinds of Fibers (Protein) • Collagen • Strong & flexible • Reticular • Fine branching fibers form supporting framework • Elastic • stong & elastic
III. Connective Tissue • D. Kinds of Cells • Fibroblast • Makes fibers & matrix • Fibrocyte • Mature fibroblast • 3. Macrophage • Defense, phagocytosis • Plasma cell • Makes antibodies
III. Connective Tissue • D. Kinds of Cells • 5. Mast Cells • Release heparin (anti-coagulant) • Release histamine (dilates small blood vessels) • 6. Fat Cells • Mature fibroblast
III. Connective Tissue E. Areolar connective tissue1. Structure • collagenous & elastic fibers • all 6 types of connective tissue cells • filmy matrix
III. Connective Tissue E. Areolar connective tissue 2. Function • Covers organs • Holds vessels & nerves in place • 2nd line of defense • Location • Mucous membranes • Under skin • Between tissues of organs
III. Connective Tissue • Structure • Collagen fibers • Fibroblasts and macrophages • Dense matrix F. Dense connective tissue
III. Connective Tissue • Function • Provide strength F. Dense connective tissue • Location • Tendons • Ligaments
III. Connective Tissue • Structure • elastic fibers • Few fibroblasts G. Elastic connective tissue • Function • Allows stretching • Location • Lungs • Trachea • Arteries
III. Connective Tissue • Structure • Reticular fibers • Thin matrix H. Reticular connective tissue • Function • Hold cells of loose organs together • Location • Liver • Spleen • Bone marrow