Program Cost and Schedule Integrated with Systems Engineering Models
300 likes | 532 Vues
Program Cost and Schedule Integrated with Systems Engineering Models . Charlie Stirk CostVision Harold P. Frisch NASA GSFC emeritus David Price Eurostep. NASA ESA Product Data Exchange Workshop, April 29-May 1, 2009. Problem Statements.

Program Cost and Schedule Integrated with Systems Engineering Models
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Program Cost and Schedule Integrated with Systems Engineering Models Charlie Stirk CostVision Harold P. Frisch NASA GSFC emeritus David Price Eurostep NASA ESA Product Data Exchange Workshop, April 29-May 1, 2009
Problem Statements • How to exchange integrated cost, schedule, and systems engineering information? • How to predict cost and schedule based on systems engineering artifacts? • Architecture – structures and interfaces • Requirements – properties and constraints • Behavior – states and functions
Elements of a Solution • Model that represents cost, schedule, engineering entities, their relationships, and model management • STEP AP233 Systems Engineering • Mapping other formats with AP233 • Reference Data Libraries for DoDAF, SysML, Earned Value Management, … • Creating neutral format for contracts • Data EXchange specification (DEX)
What Does AP233 Enable? • System modeling • Decision support • Requirements management • Measures of effectiveness • Analysis interface • Verification & Analysis • Justification • System structure • Product data management • Breakdown • Interface • System behavior • Function based behavior • State based behavior • Program management • Issue • Activities • Approvals • Risk • Probability & Consequence • Source & Impact • Contingency plans • Project • Organizational structure • Project breakdown • Schedule • Work structure • Management information resources
Document Slot handles Project has specifies Contract storage Location 239 Express-G System Breakdown Functional Breakdown Requirement Part Interface Task Product _relation View_relation Version_relation structure related related related relating relating relating required_ product Activity_method Product Product _version Product _view_definition view_of utilizes of_ product in_context Context Product_individual method_used Scheme observed_ product Observation structure schedule observed_state actual_state operates_on Product _individual_ version Activity State utilizes expected_state directive start Planned_ Product Realized_ Product Date_time finish start_state end_state in_response_to observation_consequence Work_order Work_request • STEP AP239 Product Life Cycle Support (PLCS) and 233 share over 70% of their core modules
Mapping with Reference Data • Entities/relationships 233/239 are general • E.g. Product, Activity, Product_relation • Most things are subtypes of Product • Requirement, Part, Interface, … • Other subtyping is by classification assignment • Specialization of entities/relationships/attributes • External classes of reference data • E.g. INCOSE subtypes for requirement_version • Functional, Performance, Reference, Validation, …
OASIS DEX Architecture • Reference data in Web Ontology Language (OWL) tailors to domain • Templates are assembled into Data EXchange Specification (DEX)
Extension by Subtyping ISO Information Model OASIS Taxonomy
Solid box is an instance of Activity named “Activity x” XML exchange document Is validated against Empty box is an instance of Classification XML Schema Classification says “Activity x” is classified as a “Repair” Is generated from OASIS Taxonomy ISO Information Model
Exchange Scenario translate to AP233 translate from AP233 XML exchange document classification System Engineering Tool Vendor A System Engineering Tool Vendor B Linked Taxonomy Libraries
Reference Data Issues • Need expert knowledge of STEP information models to properly subtype with reference data • Many potential sources of reference data from different domains (need domain experts involved) • Basic set theory used to classify reference data • Potential for other uses of OWL e.g. semantic reasoning
DoDAF • DoDAF - Department of Defense Architecture Framework • Views of systems engineering data • CADM - Core Architecture Data Model • Standardized database schema for DoDAF • DARS – DoD Architecture Repository System • Stores DoDAF artifacts for program analysis • UPDM – Unified (formerly UML) Profile for DoDAF and MoDAF • Support for SysML and UML
NODES A B C TIME System Functionality Description (SV-4) T1 T2 T3 Systems Functionality Sequence and Timing Description (SV-10 a/b/c) Technical Architecture Profile (TV-1) Physical Schema SV-11 Standards Technology Forecast (TV-2) Systems Evolution Description (SV-8) System - System Matrix (SV-3) Systems Interface Description (SV-1) Activity to System Function (SV-5) Systems Technical • -------------------------------- Systems Communications Description (SV-2) • ..... Operational • ..... • ..... Systems Data Exchange Matrix (SV-6) Systems Performance Parameters Matrix (SV-7) X Y X Z Y Operational Concept Description (OV-1) Y X Systems Technology Forecast (SV-9) Operational Activity Model (OV-5) Node Connectivity Description (OV-2) NODES A B C TIME T1 T2 T3 Operational Activity Sequence and Timing Description (OV-6 a/b/c) Organizational Relationships Chart (OV-4) Information Exchange Matrix (OV-3) Logical Data Model (OV-7) DoDAFViews
DoDAF Issues • Undergoing continuous improvement • Next revision to 2.0 • Multiple formats (CADM and UPDM) • Required early on for programs • Not connected with later system engineering activities • Not updated as programs evolve
DoDAF and AP233 • There exists a CADM-AP233 OWL representation (www.exff.org) • Used AP233 WD2 version with fixes, CADM 1.02 • Need to update to current version of AP233 and newer versions of CADM (1.5) • Need to map UPDM with AP233 • Current version and future versions
SysML – Systems Modeling Language • Graphical language sponsored by INCOSE/OMG
SysML Issues • XMI – XML Metadata Interchange • For UML and others expressed in OMG Meta Object Facility (MOF) • Vendor implementations incompatible • OMG Model Interchange Working Group to improve interoperability • SysML currently suited for model presentation, not exchange • Model configuration and other management is out of scope, and some provided by tool vendors
SysML and AP233 • SysML to AP233 mapping underway • Both based on INCOSE concept model • Creating reference data for SysML • SysML info a subset/subtype of AP233 • 233 enhances SysML by • Management and representation of • Risk, Analysis, Configuration, Program/Project … • Linking to downstream CAD, CAE, CAM, PLCS • EXPRESS meta-model now in MOF • 233 first test case of bringing STEP AP into OMG MDA
Context Diagram for Architecture & Systems Engineering Standards Process Standards EIA 632 ISO 15288 IEEE 1220 CMMI * Architecture Frameworks FEAF DoDAF Zachman FW MoDAF Implemented by Tools Modeling Methods HP SADT OOSE Other Modeling & Simulation Standards UML/SysML UPDM HLA Other Modeling Simulation Interchange Standards Other MOF/XMI STEP/AP-233 DoDAF UML/SysML STEP/AP-233 CADM Repository
Earned Value Management • Government contract cost and schedule performance reporting • Standards for EVM Systems • ANSI/EIA-748-A EVMS Guidelines • XML Schema based on ANSI X.12 806 & 839 • NDIA Program Management Systems Committee XML Working Group • Defense Contract Management Agency
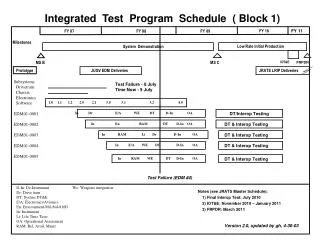
Standard Reports • Integrated Master Plan (IMP) • Integrated Master Schedule (IMS) • Contract Performance Report (CPR) • Contract Funds Status Report (CFSR)
Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) • MIL-HDBK-881 standard 3-level for weapon systems • E.g. Missile System/Air Vehicle/Propulsion • Allows trade-space • Contractor tailors to deeper levels for program • Some contractors standardizing lower WBS levels • New Operations & Support WBS
WBS Integration • Requirements and specifications by WBS • IMS uses WBS to code tasks in SOW • Contracts report task cost by WBS
EVM Status • EVM Central Repository • Required for major programs • Used for analysis • PM software vendors support • Mapping EVM into 233 • OWL Reference Data • Need to map EVM Schema and 233-based Schema • Maintains upward compatibility
233 Pulls it All Together • STEP AP233 can integrate cost, schedule and systems engineering • Models can be managed, inter-related, and linked to specialty engineering domains
Analysis from Repositories • Regression of Cost Estimating Relationships (CER) from past programs • Early work shows that the number of DoDAF interfaces correlated to cost & schedule (and growth) • Need to automate extraction and expand to other metrics and SysML • Causal Activity Based Cost Models (ABC, a.k.a. detailed engineering, bottoms-up) • Driven from requirements, system structure, behavior • Linked to IMS
Summary • STEP AP233 Systems Engineering can • Input and integrate cost, schedule, and engineering models • Manage models through changes, lifecycle, and supply chain • Provide a basis for program baseline, reporting, and analysis