Understanding Plant Cells: Structure, Functions, and Key Organelles
210 likes | 359 Vues
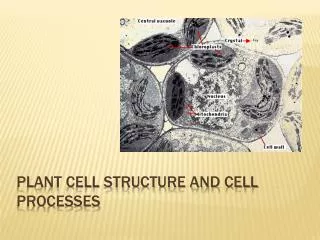
Plant cells are unique eukaryotic cells with distinctive features that set them apart from other cells. They contain specialized organelles such as the nucleus (the control center), chloroplasts for photosynthesis, and a rigid cell wall. In addition, they have structures like plasmodesmata for intercellular communication, dictyosomes for processing sugars, and vacuoles for storage. Other essential components include the endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondria for energy production, and ribosomes for protein synthesis. Understanding these features is crucial for studying plant biology.

Understanding Plant Cells: Structure, Functions, and Key Organelles
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Plant Cell By Jessica Bravo
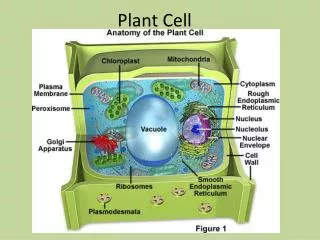
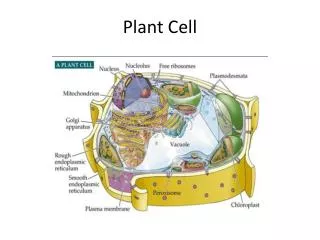
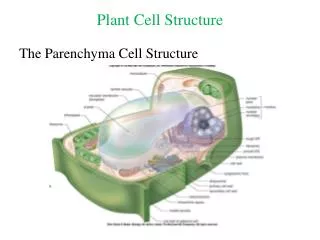
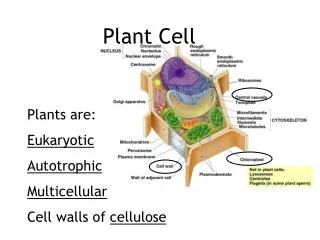
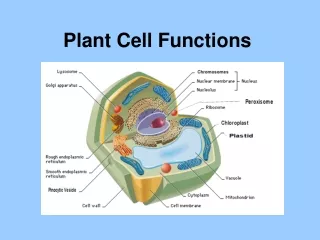
Meaning • Plant cell: are eukaryotic cells that differ in several key respects from the cells of other eukaryotic organisms. Their distinctive features include: • nucleus,Plasmodesma, Dictyosome, Dictyosome, Nucleus,Nuclear envelope, Endoplasmic reticulum, Peroxisome,Chloroplast, • Mitochondria, Cytosol,Free ribosome, Tonoplast, Vacuole, cell wall, Plasma membrane, Thylakoids, and Starch grain
Nucleus • Nucleus: a central part about which other parts are grouped or gathered.Also sometimes referred to as the "control center", is a membrane-enclosed organelle found in eukaryotic cells.
Plasmodesma • An intercellular bridge.
Chromatin • Chromatin: a coloring substance in the nucleus of the cell.
Dictyosome • Dictyosome: cellular organelle that elaborates sugars and proteins.
Nuclear Envelope • Nuclear envelope: membrane surrounding the nucleolus.
Cell Wall • Cell Wall:the definite boundary or wall that is part of the outer structure of certain cells, as a plant cell.
Endoplasmic Reticulum • Endoplasmic reticulum: a formation within the cytoplasm that plays a role in the production of various substances.
Peroxisome • Peroxisome: cytoplasmic organelle which contains enzymes.
Chloroplast • Chloroplast : granule of chlorophyll, which is needed for photosynthesis.
Mitochondria • Mitochondria : granule that plays an important role in the respiration and energy-releasing reactions in living cells.
Cytosol • Cytosol: liquid part of the cytoplasm.
Free Ribosome • Free ribosome : cytoplasmic organelle which is responsible for protein synthesis.
Vacuole • Vacuole: space with the cytoplasm of a cell containing various substances.
Tonoplast • Tonoplast : vacuolar membrane.
Plasma membrane • Plasma membrane: envelope of plasma.
Thylakoids • Thylakoids: membranous molecular structures involved in photosynthesis.
Starch Grain • Starch Grain: starch granule.