HPLC Analysis of GST-FOXO3a-HIS6 Phosphorylation by JNKs with 32P Radioactivity Detection
10 likes | 130 Vues
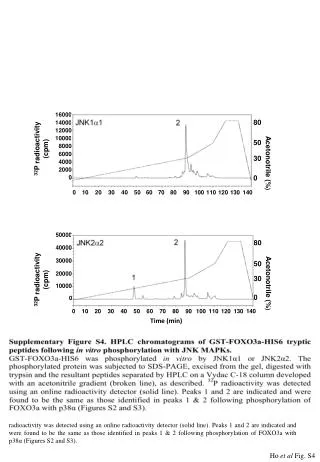
This supplementary figure (Figure S4) presents HPLC chromatograms of GST-FOXO3a-HIS6 tryptic peptides after in vitro phosphorylation with JNK1α1 and JNK2α2. Phosphorylated proteins were analyzed through SDS-PAGE, excised, and digested with trypsin. Resulting peptides were separated using a Vydac C-18 column with an acetonitrile gradient. The detection of 32P radioactivity was performed with an online detector. Key peaks match those identified earlier with p38α, demonstrating consistent phosphorylation patterns.

HPLC Analysis of GST-FOXO3a-HIS6 Phosphorylation by JNKs with 32P Radioactivity Detection
E N D
Presentation Transcript
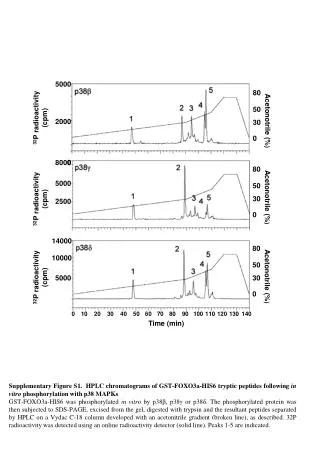
16000 80 14000 12000 10000 50 32P radioactivity (cpm) 8000 6000 30 4000 Acetonotrile (%) 2000 0 0 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 110 120 130 140 50000 Time (min) 80 40000 30000 50 20000 32P radioactivity (cpm) 30 Acetonotrile (%) 10000 0 0 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 110 120 130 140 Time (min) Supplementary Figure S4. HPLC chromatograms of GST-FOXO3a-HIS6 tryptic peptides following in vitro phosphorylation with JNKs. GST-FOXO3a-HIS6 was phosphorylatedin vitro by JNK1α1 or JNK2α2. The phosphorylated protein was subjected to SDS-PAGE, excised from the gel, digested with trypsin and the resultant peptides separated by HPLC on a Vydac C-18 column developed with an acetonitrile gradient (broken line), as described. 32P radioactivity was detected using an online radioactivity detector (solid line). Peaks 1 and 2 are indicated and were found to be the same as those identified in peaks 1 & 2 following phosphorylation of FOXO3a with p38α (Figures S2 and S3). Ho et al Fig. S4