Enlightenment Impact: Rights, Despots, Democracy
50 likes | 134 Vues
Explore Enlightenment philosophies by Locke, Hobbes, Montesquieu, Rousseau & their impact on government, censorship, enlightened despots, democracy & nationalism in the 1700s.

Enlightenment Impact: Rights, Despots, Democracy
E N D
Presentation Transcript
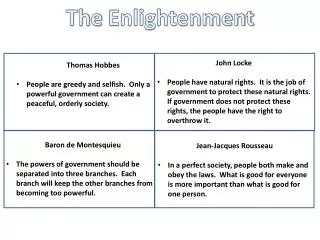
TheEnlightenment • John Locke • People have natural rights. It is the job of government to protect these natural rights. If government does not protect these rights, the people have the right to overthrow it. • Thomas Hobbes • People are greedy and selfish. Only a powerful government can create a peaceful, orderly society. • Baron de Montesquieu • The powers of government should be separated into three branches. Each branch will keep the other branchesfrom becoming too powerful. • Jean-Jacques Rousseau • In a perfect society, people both make and obey the laws. What is good for everyone is more important than what is good for one person.
Impact of the Enlightenment • Greater numbers of people began to question established beliefs and customs. • Government Censorship • As Enlightenment ideas gained in popularity, government and Church leaders worked to defend the established systems. They started a campaign of censorship to suppress Enlightenment ideas. Many writers, including Voltaire, were thrown into prison, and their books were banned and burned.
Impact of the Enlightenment • Enlightened Despots • Maria Theresa – ruler of Austria during the 1700s • Improved tax system by making nobles and clergy pay taxes • Eased the tax burden on peasants • Primary education • Joseph II – ruler of Austria • Modernized government • Appointed competent officials • Religious tolerance • Ended censorship • Implemented legal reforms
Impact of the Enlightenment • Enlightened Despots • Catherine the Great – ruler of Russia in the 1700s • Corresponded with Voltaire and Montesquieu • Asked for advice from nobles and free peasants • Built schools and hospitals • Promoted the education of women
Impact of the Enlightenment • Democracy and Nationalism • Individualism! • A belief in personal freedom, and a sense of the basic equality of human beings. • Nationalism! • As people in a country drew together to fight for a democratic government, strong feelings of nationalism arose. These ideas contributed to an age of revolution…