DNA in the Cell
280 likes | 466 Vues
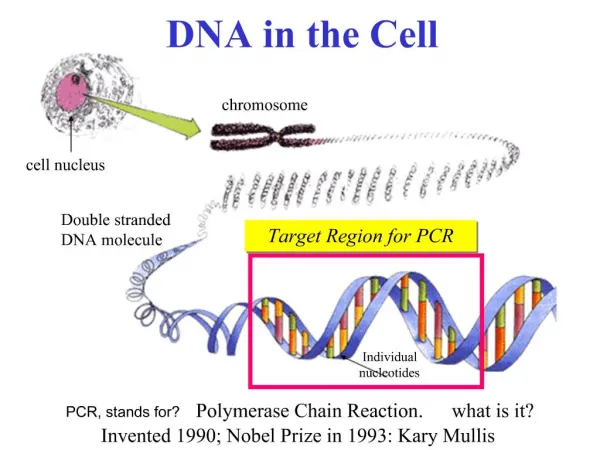
DNA in the Cell. Stored in Number of Chromosomes (24 in Human Genome) Tightly coiled threads of DNA and Associated Proteins: Chromatin 3 billion bp in Human Genome: Total genetic content of cell DNA can be replicated Genes: Specific sequence of bases (one polypeptide. Central Dogma.

DNA in the Cell
E N D
Presentation Transcript
DNA in the Cell • Stored in Number of Chromosomes (24 in Human Genome) • Tightly coiled threads of DNA and Associated Proteins: Chromatin • 3 billion bp in Human Genome: Total genetic content of cell • DNA can be replicated • Genes: Specific sequence of bases (one polypeptide
Flow of Information • DNA store a lot of information • A little bit used at a time • Small bits copied into temporary molecules • messenger RNA (mRNA) • Transcription • RNA - Single Stranded • U for T • Ribose is sugar
Coding • Sets of three letter from (A,G,C,T) codes for amino acid (codon) • Stop codons (3) • Universal language for Amino Acids
Transcription • Transcription to preserve the DNA (sense) • RNA (antisense) made by RNA Polymerase • Polymerase binds at DNA promoter sequence just before the gene • Nucleotides from environment added to RNA chain based on DNA Template • Continues until terminator sequence
Genes • 10% of DNA encodes for Genes • Exons: Coding Sequences for Proteins • Introns: Non-Coding Sequences • Human Genome: 100,000 Genes • 100,000 Proteins synthesized from genes • Genes encode for Amino Acids(Codons) • Building blocks for proteins (workers)
DNA to messenger RNA (mRNA) • Direct for prokaryotes • From Nucleus to Cytoplasm for eukaryotes • Introns removed from mRNA • Template for Protein Synthesis by Ribosome
Translation • mRNA copy to Protein • Translation: Process of Protein Synthesis • Occurs on Ribosomes: Large structures consisting of proteins and RNA • Many of them in the cell • transfer RNA (tRNA) which accomplish actual translation
tRNA • At one anticodon (three base sequence) • Complementary to one of codons on mRNA • At other end is a chemical group to attach an amino acid • Read codons, Bind to them, Bring amino acid to ribosome • Shape dependent -- Energy Consuming (50% in bacteria)
Signals for Protein Synthesis • Stop Codons • Start Codon • Beginning of mRNA sequence • Reading Frame (way message divided into codons) • AUGCCUGUCAAA • AUG CCU GUC AAA • A UGC CUG UCA AA
DNA Replication • Copy DNA for new cells • DNA Polymerases • Mistakes corrected by enzyme itself • Proofreading • Mistake 1 in 10^9