Understanding Polygons: Classifying and Calculating Interior Angles
140 likes | 256 Vues
This educational resource focuses on polygons, providing clear definitions and methods for classifying various shapes, as well as formulae to calculate the sum of their interior angles. Students will learn how to determine whether a figure is a polygon, classify it, and compute the sum of the interior angles using the formula ((n - 2) times 180), where (n) is the number of sides. Examples include determining the measures of angles in pentagons, hexagons, heptagons, and octagons, along with practical applications like real-life shapes such as stop signs.

Understanding Polygons: Classifying and Calculating Interior Angles
E N D
Presentation Transcript
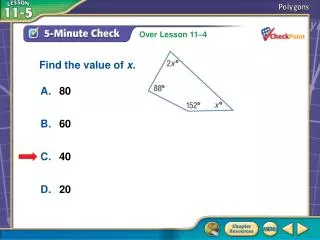
A B C D Find the value of x. A. 80 B. 60 C. 40 D. 20 5-Minute Check 2
You have already classified quadrilaterals. (Lesson 11–4) • Classify polygons. • Determine the sum of the measures of the interior angles of a polygon. Then/Now
polygon A simple closed figure in a plane formed by three or more line segments • diagonal • interior angle • regular polygon A line segment that joins two nonconsecutive vertices of a polygon An angle formed inside of a polygon A polygon having all sides congruent and all angles congruent Vocabulary
Classify Polygons Determine whether the figure is a polygon. If it is, classify the polygon. If it is not a polygon, explain why. The figure has 5 sides that only intersect at their endpoints. Answer: It is a pentagon. Example 1
A B C D Classify the polygon. A. pentagon B. hexagon C. heptagon D. octagon Example 1
Find the sum of the measures of the interior angles of a heptagon. Read the Test Item The sum of the measures of the interior angles is (n – 2)180. Since a heptagon has 7 sides, n = 7. Solve the Test Item (n – 2)180 = (7 – 2)180 Replace n with 7. = 5 ● 180 Simplify. = 900 Multiply. The sum of the measures of the interior angles of a heptagon is 900°. Answer:The answer is 900° Example 2
A B C D What is the sum of the interior angles of an octagon? A. 540° B. 720° C. 900° D. 1080° Example 2 CYP
Measure of One Interior Angle TRAFFIC SIGNSA stop sign is a regular octagon. What is the measure of one interior angle in a stop sign? Step 1 Find the sum of the measures of the angles. An octagon has 8 sides. Therefore, n = 8. (n – 2)180 = (8 – 2)180 Replace n with 8. = 6(180) or 1080 Simplify. The sum of the measures of the interior angles is 1080°. Example 3
Measure of One Interior Angle Step 2 Divide the sum by 8 to find the measure of one angle. 1080 ÷ 8 = 135 Answer: So, the measure of one interior angle in a stop sign is 135°. Example 3
A B C D PICNIC TABLE A picnic table in the park is a regular hexagon. What is the measure of one interior angle in the picnic table? A. 720° B. 128.57° C. 120° D. 108° Example 3 CYP