Spreadsheets vs. Databases
120 likes | 406 Vues
Spreadsheets vs. Databases. for data storage. Commonality. Can store some data Can sort data Can query information. It’s very easy to pick the wrong application. What is a Spreadsheet?.

Spreadsheets vs. Databases
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Spreadsheets vs. Databases for data storage
Commonality • Can store some data • Can sort data • Can query information It’s very easy to pickthe wrong application
What is a Spreadsheet? A spreadsheet is a programthat enables you to store, manipulate, and graphically represent numeric data.
What are the characteristicsof a Spreadsheet? • Data items are often interdependent • Changing one value may trigger changes in another value • Provides great mathematical and statistical functions • “What if” scenario support • Solver support • What value has to change to produce a given result? • Excellent graphics and charting abilities • Easy to learn – intuitive interface
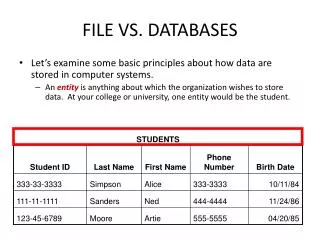
What is a Database? A database is an integrated collection of logically related data elements.
Characteristics of a Database… • are designed to share. • Two or more people can edit a database at the same time. • are safe. • Databases write data to the hard drive immediately. • can handle large amounts of data efficiently. Much more efficiently than Excel. • Are easy to link tables of related data together. • Trying to accomplish this in Excel can be unwieldy and invites errors.
Why use a databaseto store data? • Need multi-user access • Keep your data safe • Preserve data integrity, use data validation • Eschew Obfuscation • Avoid redundancy and confusion • Data can be updated in one place and only takes up as much space as needed
Spreadsheets are NOT well suited for collaboration, data quality or regulatory compliance. Spreadsheets often contain substantial and material errors. Case Study - Magellan Loses Its Compass Why not use a Spreadsheet? (for data storage)
Organizations are starting to look at the problems the misuse of spreadsheets is causing but it’s not an IT priority. “Spreadsheets are growing like weeds, but they may be a liability in the Sarbanes-Oxley era.”–Alan Horowitz
The Sarbanes-Oxley Act The single most important piece of legislation affecting corporate governance, financial disclosure and the practice of public accounting since the US securities laws of the early 1930s. Was created to protect investors by improving the accuracy and reliability of corporate disclosures after a wave of accounting scandals (Enron, Tyco, WorldCom) Signed into law on 7/30/02 by President Bush Requires companies to maintain a good audit trail. Generating such a trail is often difficult to do with Excel.
Use Spreadsheets for: • Complex computations on smaller set of data. • What if analysis • Solver Supported - Decision Making • Work in progress • Standalone work in progress projects (ones not involving collaborative efforts)