Example – see Example 21.2 from course text
60 likes | 178 Vues
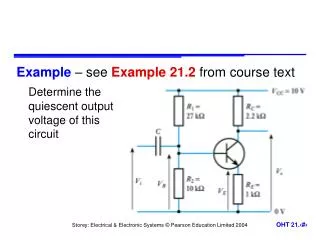
Example – see Example 21.2 from course text Determine the quiescent output voltage of this circuit. Base current is small, so Emitter voltage V E = V B – V BE = 2.7 – 0.7 = 2.0 V Emitter current Since I B is small, collector current I C I E = 2 mA

Example – see Example 21.2 from course text
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Example – see Example 21.2 from course text Determine thequiescent outputvoltage of thiscircuit
Base current is small, so Emitter voltage VE = VB – VBE = 2.7 – 0.7 = 2.0 V Emitter current Since IB is small, collector currentIC IE = 2 mA Output voltage = VCC – ICRC = 10 - 2 mA 2.2 k = 5.6 V
A common-collector amplifier • unity gain • high input resistance • low output resistance • a very goodbuffer amplifier
21.7 Other Bipolar Transistor Applications • A phase splitter