CHAPTER 8 Mitosis SP 2013
410 likes | 433 Vues
Learn about the cellular growth process and the stages of mitosis in this educational guide. Discover how cells reproduce and regulate their cell cycle.

CHAPTER 8 Mitosis SP 2013
E N D
Presentation Transcript
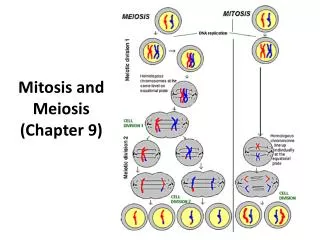
Chapter 9 Cellular Reproduction Section 1: Cellular Growth Section2: Mitosis and Cytokinesis Section 3: Cell Cycle Regulation
Cellular Reproduction Chapter 9 9.1 Cellular Growth Ratio of Surface Area to Volume
Cellular Reproduction Chapter 9 9.1 Cellular Growth • As the cell grows, its volume increases much more rapidly than the surface area. • The cell might have difficulty supplying nutrients and expelling enough waste products.
Cellular Reproduction Chapter 9 9.1 Cellular Growth Transport of Substances • Substances move by diffusion or by motor proteins. • Diffusion over large distances is slow and inefficient. • Small cells maintain more efficient transport systems.
Cellular Reproduction Chapter 9 9.1 Cellular Growth Cellular Communications • The need for signaling ______to move throughout the cell also limits cell _____. • Cell ____ affects the ability of the cell to communicate instructions for cellular functions.
Cellular Reproduction Chapter 9 9.1 Cellular Growth The Cell Cycle • ___ ________ prevents the cell from becoming too large. • It also is the way the cell reproduces so that you grow and heal certain injuries. • Cells reproduce by a cycle of growing and dividing called the ___ _______.
Cellular Reproduction Chapter 9 9.1 Cellular Growth • __________ is the stage during which the cell grows, carries out cellular functions, and replicates. • _________ is the stage of the cell cycle during which the cell’s nucleus and nuclear material divide. • ___________is the method by which a cell’s cytoplasm divides, creating a new cell.
Cellular Reproduction Chapter 9 9.1 Cellular Growth The Stages of Interphase • The first stage of ____________, G1 • The cell is growing, carrying out normal cell functions, and preparing to replicate DNA.
Cellular Reproduction Chapter 9 9.1 Cellular Growth The Second Stage of Interphase, S • The cell copies its _____in preparation for cell division.
Cellular Reproduction Chapter 9 9.1 Cellular Growth The Third Stage of Interphase, G2 • The cell prepares for the division of its nucleus.
The process of asexual reproduction begins after a sperm fertilizes an egg.
Three reasons why cells reproduce by asexual reproduction: 1. ________ 2. ________ 3. ________________ Skin cancer - the abnormal growth of skin cells - most often develops on skin exposed to the sun. Cell that reproduce by asexual reproduction reproduce constantly.
Animated Mitosis Cycle http://www.cellsalive.com/mitosis.htm • Interphase • Prophase • Metaphase • Anaphase • Telophase & Cytokinesis
Interphaseoccurs before mitosis begins • Chromosomes are ___________(# doubles) • Chromosomes appear as threadlike coils (____________) at the start, but each chromosome and its copy(_______ chromosome) change to sister chromatids at end of this phase CELL MEMBRANE Nucleus Cytoplasm
Interphase Plant Cell Animal Cell Photographs from: http://www.bioweb.uncc.edu/biol1110/Stages.htm
Prophase 1st step in Mitosis • Mitosis begins (cell begins to divide) • ___________(or poles) appear and begin to move to opposite end of the cell. • Spindle fibers form between the poles. Centrioles Sister chromatids Spindle fibers
Prophase Plant Cell Animal Cell Spindle fibers Centrioles Photographs from: http://www.bioweb.uncc.edu/biol1110/Stages.htm
Metaphase 2nd step in Mitosis • ____________(or pairs of chromosomes) attach to the spindle fibers. Centrioles Spindle fibers
Metaphase Plant Cell Animal Cell Photographs from: http://www.bioweb.uncc.edu/biol1110/Stages.htm
Anaphase 3rdstep in Mitosis • ______________(or pairs of chromosomes) separate and begin to move to opposite ends of the cell. Centrioles Spindle fibers
Anaphase Plant Cell Animal Cell Photographs from: http://www.bioweb.uncc.edu/biol1110/Stages.htm
Telophase4th step in Mitosis • Two new ________ form. • Chromosomes appear as chromatin (threads rather than rods). • Mitosis ends. Nuclei Nuclei Chromatin
Telophase Plant Cell Animal Cell Photographs from: http://www.bioweb.uncc.edu/biol1110/Stages.htm
Cytokinesisoccurs after mitosis • Cell membrane moves inward to create two daughter cells – each with its own nucleus with identical ________________.
- Cell Division The Cell Cycle 32
MitosisAnimation http://www.cellsalive.com/mitosis.htm
Cellular Reproduction Chapter 9 9.3 Cell Cycle Regulation Normal Cell Cycle • Different __________ combinations _______ other activities, including DNA ___________, protein _____________, and nuclear ___________ throughout the ______ ______________.
Cellular Reproduction Chapter 9 9.3 Cell Cycle Regulation _____________ __________ Checkpoints • The cell _________________ has built-in ___________ that _____________ the cycle and can __________ it if something goes __________. • ______________ checkpoints also have been identified in ____________.
Cellular Reproduction • Cancer cells can ___ an __________ by ________ out _____ cells, resulting in the _______ of tissue _________. Chapter 9 9.3 Cell Cycle Regulation ______________ Cell Cycle: ___________ • __________ is the __________ growth and _______ of cells.
Cellular Reproduction Chapter 9 9.3 Cell Cycle Regulation ___________ of Cancer • The __________ that occur in the ___________ of cell ________ and _________ of cancer cells are due to ___________. • Various _____________ factors can ________ the occurrence of ________ cells.
Causes of Cancer • ___________________ • ___________________ • ___________________
Cellular Reproduction Chapter 9 9.3 Cell Cycle Regulation Apoptosis • _______________ cell __________ • __________ going through apoptosis actually _________ and _________ in a ____________ process.
Cellular Reproduction Chapter 9 9.3 Cell Cycle Regulation Stem Cells • ____________ cells that can _______ into __________ cells when _____ the right ____________
Cellular Reproduction Chapter 9 9.3 Cell Cycle Regulation Embryonic Stem Cells • After ___________, the resulting ______ of cells _________ repeatedly until there are about _____-____ cells. These cells have ________ become _____________.
Cellular Reproduction Chapter 9 9.3 Cell Cycle Regulation Adult Stem Cells • Found in _________ tissues in the body and __________ be used to _________ and ___________ the ________ kind of tissue • _________ controversial because the adult stem cells can be ____________ with the ___________ of their donor Cellular Reproduction