Contraceptive Failure Rates and Methods: Overview of Effectiveness and Considerations
200 likes | 339 Vues
This article explores the failure rates of various contraceptive methods used in the USA, including female sterilization (27%), oral contraceptives (26%), and male condoms (20%). It discusses natural family planning techniques, including calendar methods and the symptothermal method, which account for ovulation timing and sperm viability. Additionally, it examines barrier methods like condoms and diaphragms, as well as intrauterine devices (IUDs) with copper or hormonal components. Health benefits and risks of combined oral contraceptives are also reviewed.

Contraceptive Failure Rates and Methods: Overview of Effectiveness and Considerations
E N D
Presentation Transcript
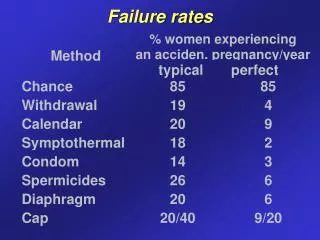
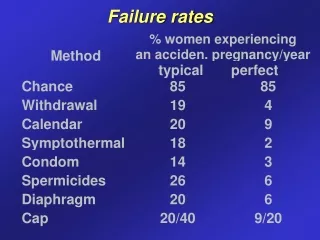
Contraceptive use - USA • Female sterilization 27% • OC 26% • Male condom 20% • Male sterilization 10% • Withdrawal 3% • Injectable (MPA) 3% • Diaphragm 2% • Implants 2% • IUD 1%
Natural family planning • identification of potentially fertile days + periodic abstinence • calendar - assumption: • ovulation on day 14 (± 2) of menstrual cycle • sperm viability 5 days • oocyte viability 24 hours • abstinence days 9-15 (7-17) • failures even with regular cycles, does not account for additional factors (stress, illness, travel) • does not work well for women with irregular cycles, chronic cervicitis/vaginitis
Natural family planning • BBT method: daily temperature readings; temperature rise by 0.4 C/F after ovulation • Cervical mucus (Billings) method: observation of the cervical secretions: fertile days - increase in secretions that are clear , strechy and slippery • Symptothermal method: combination of the fertility indicators (cervical mucus, BBT and/or calendar) Home ovulation detection kits (urinary LH)
Lactational amenorrhoea method • Baby less than 6 months • Amenorrhoea since lochia ceased • Fully or nearly fully breastfeeding 2% chance of pregnancy
Barrier methods • Male condom (latex, polyurethane) • Female condom (polyurethane Reality) • Diaphragm (6h/6h, not longer than 24h TSS, UTI) • Cervical cap (up to 48h, spermicide necessary, Prentif cap) • Spermicides (films, gels, foams, suppositories; nonoxynol-9 2-12%- surfactant that destroys cell membrane; protective against STI)
IUD • With copper (Copper T380): • sterile, inflammatory, hostile endometrial environment • inhibits sperm migration • inhibits fertilization and oocyte transport • With LNG (Mirena): as above PLUS • thickens cervical mucus • augments atrophic decidualization of endometrium • ? may inhibit ovulation
IUD • Appropriate selection • Contraindications: • acute PID / history of PID • genital bleeding of unknown etiology • known/suspected uterine or cervical malignancy • decreased immunoresistance (leukemia, AIDS) • allergy to copper • distortion of the uterine cavity • multiple sex partners
IUD • NOT an abortifacient • DOES NOT increase the risk of ectopic (actually decreases the risk) • DOES NOT increase the risk of PID • DOES NOT increase the risk of subsequent infertility • DOES NOT increase the risk of cervical and uterine cancer
DMPA injections • IM injection every 3 months (150mg of DMPA) • blocks LH surge and prevents ovulation • side-effects: menstrual changes (irregular bleeding , amenorrhoea)
Subdermal implants • Norplant I : 5 year LNG implant system (six tubes; 85ug of LNG daily, by year 5 30ug) • Norplant II (Jadelle) : 3 year 2 rod system • Implanon : (single implant with 3-keto-desogestrel, 3 year) • side-effects + difficulties with removal
Combined oral contraceptives COC • 20-50 ug of EE • progestin: • desogestrel, norgestimate, gestodene • LNG, Norethisterone (NET, NETA) • monophasic : constant dose of E and P • biphasic and triphasic : mainly variation of P dose (also E dose possible) • used by 30-40% of reproductive age women in Western Europe
Combined oral contraceptives COC • prevent ovulation by suppression of pituitary LH/FSH secretion • additional P effects: • changes in the cervical mucus hindering sperm transport • changes in the endometrium: prevention of implantation • decreased tubal motility : delayed oocyte transport
COC - health benefits • Ovarian cancer: risk reduction by 40-80% • Endometrial cancer: risk reduction by 50% • Benign breast conditions ( risk) • PID ( risk) • Ectopic pregnancies ( risk) • Functional ovarian cysts ( risk) • Menstrual effects: improvement in regularity + anemia + dysmenorrhea • Bone density • Acne
COC - health risks • Breast cancer: small or no increase • Cervical neoplasia: increase in cervical adenocarcinoma, does not increase the risk of invasive cervical cancer • VTE: 2-3 fold increased risk (0.4 to 1.0 per 10.000 women, but in pregnancy 6 per 10.000) • MI: no increase in the risk (only for the smokers > 35 years) • stroke: no increase in the risk with low dose COC in nonsmoking women
COC - contraindications • Appropriate selection • Contraindications: • thromboembolic disorder (active or past) • coronary artery/ cerebral vascular disease • carcinoma of the breast • carcinoma of the endometrium or other estrogen-dependent neoplasia • active hepatic disease • pregnancy • smoking after 35 years of age
COC - side effects • nausea • bloating • menstrual changes • breast tenderness • ?? headache • ?? weight gain
Progestin only pills (POP) • Indications - can not tolerate E or contraindications: • breastfeeding women • postpartum women • older women with CVD • women at increased risk for VTE • NET or LNG • no delay (even hours not allowed) in administration
Emergency contraception • Immediate IUD • Yuzpe method: 72h, efficacy max. 24h; 2 pills 250ug LNG + 50ug EE (Ovran) followed by further two tablets 12 hours later • LNG alone (POEC): 750ug LNG stat and 750ug LNG 12h later; 72h, efficacy max. 24h; more effective than Yuzpe, fewer side effects (nausea+vomiting)