Utility Data Warehouse UDW 200
390 likes | 593 Vues
Mats Werner UTUA/NDF. Utility Data Warehouse UDW 200. Presentation in One-line diagrams. Presentation as Trends & Historical information. Data mining and other analysis tools. Presentation in Reports & spreadsheets. Vedlikeholdsplaner: Region Syd. Region/Område. Status. Region Syd.

Utility Data Warehouse UDW 200
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Mats Werner UTUA/NDF Utility Data WarehouseUDW 200
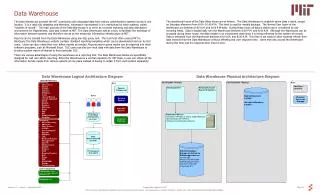
Presentation in One-line diagrams Presentation as Trends & Historical information Data mining and other analysis tools Presentation in Reports & spreadsheets Vedlikeholdsplaner: Region Syd Region/Område Status Region Syd Type Alle Alle Stasjon/Linje Spenning Skala Alle 300kv Uker 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 1996 1 8 15 22 29 5 12 Nr Stasjon/Linje Anl.Del Årsak Status Juli August 96S432-1 Hasle 10 G2 Ombygging I Gang 96S530-2 Flesaker G1 Årlig Revisjon Utsatt 96S532-1 Lysebotn F1 Mekanisk OK Reg. 96S541-1 Rendalen G3 Utskifting OK Land UDW 200 Lukk Detaljplan Ny plan Utskrifter Hjelp Data Warehouse 10.25.32 B9 B8 Station A C1 C2 T1 T2 B1 B2 Based on... B7 SPIDER SCADA/EMS/DMS C7 B4 B3 B5 B6 other Utility Information Systems SPIDER Utility Data Warehouse Data Warehouse for storage of all kinds of data
UDW – Utility Data Warehouse • Oracle-based Data Warehouse for Utility data • Able to store the continuous inflow of data from the power process • Able to store information from any other Utility Information System • Makes all this data available for Data Mining. • High User Performance • High Availability • High Redundancy
Non-real-time Information Systems Real-Time Network Management Systems AMS Oracle RDB ERP EMS BMS DMS CIS … SCADA Utility Data Warehouse UDW – Utility Data Warehouse Both Utility-wide Data Warehouse and on-line Historian! Decision Support in Office Environment Historical Analysisin Control Room Environment
Utility Data Warehouse – Original Requirements • RDBMS supporting the latest SQL standard • ”Ad Hoc” queries, ”Data Mining”, etc. • Continuous operation • Availability > 99.96 % • Redundancy • Continuous inflow of data (every 10 sec, 24h/day) • Response times (incl. picture presentation): 3-5 seconds • Extremely large database tables: > 500 million rows • Continuous calculations • sum, max, average etc. • Complex calculations using MatlabTM • Automatic archiving of data that should not be retained on-line • On-line backup • Automatic maintenance of the database • eliminates the need for a DBA at the customer
Relational Analysis • The ability to analyze relations between data is the basis for Decision Support and Data Mining • Relational Database Design makes this easy Example: ”Give me the name and the location of all lines that has been in alarmed state during the weekend ”
UDW - Open but integrated in SPIDER concept • UDW is a completely open system • UDW is also a well integrated product in the SPIDER concept … as shown in the following areas: • Open Commercial Tools and Interfaces • Application Programming Interface, API • Well Integrated in SPIDER • Powerful Database Structure • UDW as an integration platform
UDW - Open Commercial Tools and Interfaces • Based on Oracle • Oracle is an open commercial relational database • delivering ”the industry's highest performance, reliability and security for thousands of popular applications” • All tools applicable for Oracle is also applicable for UDW • Possibility to access UDW data directly in Oracle, using SQL or Oracle tools • New development in Oracle means increased value of UDW • Open interfaces • ODBC/JDBC • Microsoft COM • SQL*Net • UDW API (see below)
UDW Application Programming Interface, API • Simplifies access to UDW data • From C, C++, Java or Microsoft COM-based applications • Simplifies the creation of custom user applications • Functions for inserting and reading many data points at once • General browser routines, to access data without knowing the data model • An Oracle-independent general database server service, • for remote SQL access without SQL*Net • Implements Additional functionality • User-friendly access routines for setting and getting a range of time-series data • When data is stored by event, the data is retrieved as if it was stored cyclically • Implements support for Daylight Savings Time, Seamless Data Retrieval and Data Sets (as described later in the presentation) • The UDW API is used when: • accessing UDW data in the SPIDER environment • accessing UDW data through the Microsoft COM interface • accessing UDW data in dedicated programs (including UDW-internal)
UDW - Well Integrated in SPIDER • UDW data can be presented in SPIDER pictures, • on-line diagrams • the report and trend tools used in SPIDER • The object oriented Data Engineering for the UDW is integrated with SPIDER Data Engineering. • The UDW programs are monitored by SPIDER • Alarms and warnings from UDW are sent to SPIDER alarm list • e.g. if the data sampling is not functioning properly due to network or hardware problems
UDW - Powerful Database Structure • Data is stored in a user-friendly way • Uncompressed in open Oracle tables • Database views to simplify common queries • Data model is temporal • history of each object exist in the database • calculation algorithms related to certain objects are time-stamped • Network relations and calculations are therefore correct even when studying old data, e.g. data restored from off-line archives • Very good performance regardless of system and database size, • By the use of the Oracle partitioning technique • Sampling schemes are easily defined using Object Types and Patterns
UDW – Object Types and Patterns • Sampling schemes defined in Object Types • Each Object Type corresponds to one Oracle Table • An object to be sampled refers to a Pattern • A Pattern refers to a number of Object Types • Enables easy set-up of sampling schemes for sampled objects Object Types Objects to be sampled UDW patterns sampled Object Types calculated Object Types Measurement pattern 1 10 sec measurands 1 min average measurands Measurement pattern 2 indications by event hourly minimum measurands state estimator result daily maximum measurands Indication pattern For each Object Type is defined: • Sampling method cyclically – including sampling frequency by event – with our without integrated dead band • Retention period • If it shall be archived when retention period is over
UDW as and Integration Platform (example) Platform for application development and cross-platform integration • Developing a simple application in MS Excel, using the UDW COM interface • Combine the data in the Utility Data Warehouse with the functionality of Excel: • Visual Basic programs • Excel spreadsheet functions • Excel Charts
10.25.32 B9 B8 Stations Objects Information and relations between real-world objects Station A C1 C2 T1 T2 Sub- systems B1 B2 B7 10 sec measurands Object Types: values related to sampled real-world objects 1 hour average C7 B4 B3 B5 B6 Real-world objects daily maximum UDW - Data Model • Sampled data is stored in Object Types • A simple Power System model is also provided • including e.g. stations, sub systems, point classes • To enable queries and selections based on relational criteria • e.g. ”show all measured values included in station named AMHERST” • Automatically populated from SPIDER Data Engineering • Temporality is provided • Additional data relations possible to define easily • Since an open relational database technology is used
UDW - Data Sampling • Virtually any type of information can be stored in the UDW • The actual sampling is highly dependent on the source system from which the data is extracted. • SPIDER SCADA/EMS/DMS Sampling • All types of data in the SPIDER real-time database Avanti can be sampled and stored in the UDW database. • Cyclically, according to a user-defined sampling rate. • “By Event" (upon change), with or without an integrated dead band • Sampling from other Information Systems • There are several ways to store data into UDW: • Direct SQL insert, e.g. through database links (assuming an RDB source) • Direct access through open interfaces (e.g. ODBC, JDBC, Microsoft COM) • Dedicated program that uses the UDW API • Dedicated program that uses the ”bulk data inserter” (as used in SCADA-sampling) • Access through Avanti (e.g. by first inserting data into Avanti)
UDW – By Event sampling, integrated dead band • Sampling data By Event with an integrated dead band • a threshold value in percent of the measurement range is defined • measured value changes are accumulated between samples • if the actual value differs only slightly from the latest stored, it will thus eventually be sampled anyway
UDW - Quality Marking • UDW handles quality information together with all sampled values. • propagates automatically through all calculations • validity of calculation result depends on quality of included values • according to what is defined in Data Engineering • Mapping of quality states is defined in Data Engineering • For SPIDER sampling these mappings are set by default, but are configurable. • Possible to distinguish quality information generated in UDW and quality information originating from the SPIDER Avanti database. Original quality value Quality value in UDWafter manual correction in UDW Quality value in UDWafter calculation (a+b)
UDW - Post Disturbance Review • The Post Disturbance Review, PDR, function allows the user to monitor the process behavior before, during, and after a disturbance • A disturbance recording can be manually triggered by an operator • It is possible to playback the recorded disturbance data in a Single Line diagram. • Upon operator request, data for completed disturbances can be saved on the off-line medium used for archiving In the DE tool it is specified: • which data is to be monitored, • which events that will trigger a PDR • time periods • the number of areas available for storage of disturbance information
UDW - Data Archiving • For each Object Type it is defined (in Data Engineering): • how long it shall be retained on-line in the database • if it shall be archived • When retention period has passed, data is automatically exported to the chosen off-line medium • UDW maintains a library system for the archived data. • When data shall be restored the user specifies the type of data and for which time interval the data shall be restored • Seamless presentation is supported • If restored data and on-line data connects in time • Standard software can be used for the Archiving function. • such as Legato NetworkerTM
UDW - Advanced Data Processing • Powerful and versatile data processing capabilities • Times series calculations: • Sum, Average, Max, Min • Snapshot calculations • Any formula/calculation on objects for a certain point of time • Custom calculations • Any formula/calculation on objects for many points of time • MatlabÔ used as calculation engine • All power of the Matlab tool is available for utilization • Calculation wizard to ease simple calculation definitions • Complete ROLAP1 aggregation support (configurable) • Data can be automatically aggregated in all dimensions • E.g. summary for e.g. a station or the whole power network • Raw data and processed data are stored and handled the same way, i.e. both can be used for e.g. data mining • Automatic recalculation of all2 formulas • Both during sampling and at manual entry • Quality coding of all values • Propagates through calculations • Calculation patterns (“templates”) • For easy connection of sampled objects to a set of pre-defined calculationsand sampling profiles 1ROLAP = Relational On Line Analytic Processing 2Restrictions apply on custom calculations to prevent recursive deadlocks
Presentation in One-line diagrams Presentation as Trends & Historical information Presentation in Reports & spreadsheets Vedlikeholdsplaner: Region Syd Region/Område Region Syd Type Alle Status Alle Stasjon/Linje Spenning Skala Alle 300kv Uker 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 1996 1 8 15 22 29 5 12 Nr Stasjon/Linje Anl.Del Årsak Status Juli August 96S432-1 Hasle 10 G2 Impinging I Gang 96S530-2 Flesaker G1 Årlig Revisjon Utsatt 96S532-1 Lysebotn F1 Mekanisk OK Reg. 96S541-1 Rendalen G3 Utskifting OK Land Lukk Detaljplan Ny plan Utskrifter Hjelp Data mining and other analysis tools 10.25.32 B9 B8 Station A C1 C2 T1 T2 B1 B2 B7 C7 B4 B3 B5 B6 Database (Oracle) UDW 200 UDW - Report and user interaction functions • UDW data is easily accessed from various client tools • There are four main access routes: • Through SPIDER (historical data originating from SPIDER can be presented in SPIDER trends and spreadsheet reports, and in one-line diagrams). • Direct SQL read (through SQL*Net, Oracle tools, Microsoft Query etc.) • Direct access through open interfaces - ODBC, JDBC, COM, (e.g. Microsoft Office programs). • Through the API or Java API (dedicated programs accessing UDW data)
UDW – Client example: SPIDER Time Tagged Trends • The Time Tagged Trend (TTT) function is used for presentation of historical data in curve diagrams. • Up to 16 curves in each diagram • each with its own value axis. • Automatic scaling of value axisdepending on curve values. • The values can be fetched from different object types • Can have time offsets rela-tive to each other. • Quality coding
UDW – Client example: SPIDER Single Line Diagram • UDW data can be shown in the Single Line Diagram • by selecting a historic time and an Object Type or a Data Set. • Possible to start a replay of the data • using tape-recorder like controls: play, advance, rewind, stop • the selected time is automatically changed with a given speed.
UDW – Client example: Microsoft Excel • There are several ways to get UDW data into Excel: • via the SPIDER Excel add-in • directly through the Oracle ODBC driver • copy/paste or export/import data retrievedwith another tool, e.g. Oracle™ Browser • use the UDW COM-interface in an ExcelVisual Basic program, that reads the approp-riate information from UDW • Once the data is in Excel, its built-in functions can be used • i.e. data can be calculated on, charts can be created etc.
UDW – Client example: Microsoft Query • Using the Microsoft Query tool it is possible to create custom queries to the UDW in a user-friendly way, from the Windows environment
UDW – Client example: MATLABTM Graphics • Using the integrated MatlabTM server it is possible to define advanced formulas and calculations • Using a MatlabTM client tool it is also possible to benefit from the advanced graphical user interface of MatlabTM, and that way visualize data and corre-lations found in UDW data.
UDW - Data Sets • The Data Set function facilitates presentation of UDW data • Groups a set of Object Types • Can thereafter be referenced as one identity • A Data Set may include object groups from different SPIDER concepts: Measurands, Process values, Indications etc. • Practical e.g. when presenting historical data in Single Line diagram
10 second 1 minute tn t1 t2 t3 1 hour UDW - Seamless Retrieval – Data Set example • Measured values are often sampled with several frequencies, where higher frequency normally corresponds to a shorter retention period • Each sampling frequency corresponds to one Object Type • For some points of time there may exist data in more than one Object Type • By creating a Data Set of these Object Types, it is possible to • address the sampled values as one entity • get best possible resolution for all points of time Data that are retrieved when asking for data from t1 to tn: • t1-t2 1 hour values • t2-t3 1 minute values • t3-tn 10 second values
UDW - Daylight Saving Time Calendar time is normal time with Daylight Savings offset • The UDW has full support for Daylight Savings Time. • It is possible to store both normal time and calendar time in UDW. • It is recommended for most usages to only store normal time and let the UDW API take care of the DST conversions. • If the times are retrieved through the UDW API, the UDW takes care of the conversion • both when it comes to individual points of time and larger time spans. • The calendar time is used in display pictures and reports The UDW API is used when accessing UDW data in the SPIDER environment, by the MS COM interface and when accessing UDW data in dedicated programs Example: If the user wants to get data for a time span that includes a switch between normal time and Daylight Savings Time, there will be the correct number of times retrieved (e.g. an extra hour if going from daylight savings to normal time).
Number of sessions Max CPU per session Connect time during session etc. Database creator System administrator UDW - Authority • UDW uses standard Oracle™ authority routines • Users are assigned to a Profile and one or more Roles • Roles provides specific access rights • Profiles are used to set session parameters • Such as the maximum CPU time for a session • Examples of Roles defined in UDW: • system administrator, privileged user, common user, etc. Profiles are used to limit the risk for low priority users or user groups to impair the performance of the UDW database by using badly formed SQL-statements, for instance, a full table scan. Profile User Role
UDW - Audit Trail • The Audit Trail function in UDW tracks all changes made in the UDW database • For all manual updates the following data is stored: • old and new value • the affected time and object identity • the point of time of the modification • an operator identification • The standard Oracle™ audit trail function can also be used • providing tracking of user actions on a table level. • Tracking of insert is not recommended • the insert rate is very high in the system, and auditing insert would degrade performance.
UDW – Planned Values • The UDW supports storage of planned values • A ”window” of future data points are a opened for storage • Can be used to store e.g. forecasts or schedules • Defined as an Object Type in Data Engineering • Handling of retention period, archiving etc. just like other Object Types • A number of parameters are possible to define: • if the values shall be overwritten by actual sampled values or not • if the values shall initially be set to blank or ”invalid” • the size of the ”window” – the time span to be opened in the future • initial time period of the plan, i.e. including historical times
UDW - Data Engineering • The Data Engineering of the UDW is object oriented and dialog driven. • Is totally integrated with the Oracle-based SPIDER data engineering tool. • All data engineering logic for UDW is contained within the UDW product.
UDW – Specification of Object Types • For sampled Object Types: • sampling method: by event (including dead band) or cyclically (including frequency) • retention period, i.e. how long the object shall be retained on-line in the database • mapping between the source system (SCADA) and UDW quality codes • properties to be sampled from source system (SCADA) to UDW • for instance the actual value and updated flag for a measured value • For calculated Object Types: • source Object Type (a sampled Object Type or another calculated Object Type) • type of calculation (e.g. Average, Sum, Max, Min) • required percentage factor of valid source data to get a valid result • if time stamping shall be in the beginning or end of the calculated period
Oracle RDB Utility Data Warehouse UDW - Backup and recovery • For safety copy reasons the on-line data in UDW can be backed up, using standard Oracle™ functionality. • The backup is done in a way so that all data, including calculated values, are consistent. • The interval between backup activities is configurable • UDW Safety Backup and UDW Archiving are complementary functions! UDW Safety Backup Archiving of a safety backup of on-line data UDW Archiving Archiving of data older than retention period UDW on-line system
UDW - Configuration • The UDW can be configured in different ways to provide the required degree of redundancy and data security. • Data Redundancy • The data in the UDW database is stored redundantly so that if one disk fails, no data is lost • To get full data redundancy, RAID disks of type 0+1 are used • striping of data and disk mirroring is applied • Server Redundancy • The UDW servers are redundant so that if one UDW server becomes inoperable (e.g. due to hardware errors) another server is taking over. • Different configurations are applicable depending on the requirements on allowable downtime and loss of data during switch-over. • Redundant Server solutions, with automatic switchover • Emergency Center solutions, with manual switchover • Single Server solutions
UDW - Redundant Server solution • Redundant Server solution • No single point of failure • Automatic switchover when the on-line server malfunctions • Separate server for Safety Backup and Archiving • The two UDW servers are connected in a cluster configuration • Both servers receive data to be stored from the sampled system. • One of the servers is on-line while the other is hot standby and ready to take over the processing. • The on-line server updates the UDW database with the sampled data and calculation results
UDW – Emergency Center solution • Emergency Center solution • No single point of failure • Manual switchover when the on-line server malfunctions • Original UDW rebuilt by restoring a safety backup • The standby server is kept up-to-date with the on-line server, using Oracle Standby • It is possible to restart the standby database as the primary UDW database with minimal loss of time and data.
Disk UDW Server SCADA/EMS/DMS Shelf SCSI LAN UDW – Single Server solution • Single Server solution • With either RAID or disk shelf or RAID • If a disk shelf is used instead of RAID, the single disk controller is located in the UDW Server