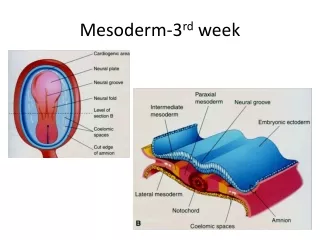
Mesoderm-3 rd week
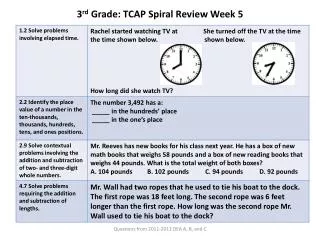
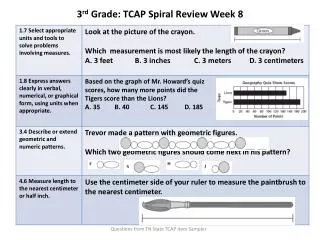
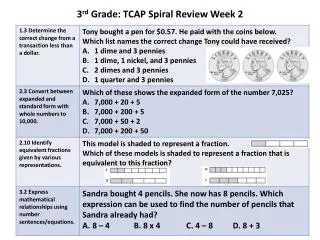
880 likes | 948 Vues
Mesoderm-3 rd week. Pronephros & mesonephros-4 th week. Urogenital ridge 4 th week. Urinary system-4 th week. 4-5 week. Mesonephric vesicle. Mesonephric tubules. metanephros. Metanephric kidneys. Metanephric kidneys. 5 th week. 6 th -7 th week. 8 th -9 th week. 12 th week.

Mesoderm-3 rd week
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Renal anomalies • Renal agenesis – Potter Sequence • Renal dysplasias – multicystic dysplastic kidney • Cong. polycystic kidney D. • Autosomal dominant • Autosomal recessive • Duplication of ureter
Renal AnomaliesDisorders due to malrotation Often associated with ectopic kidneys • Malrotated kidneys • Supernumerary kidneys • Fused kidneys- crossed renal ectopia • Divided kidney with bifid ureter
Renal AnomaliesDisorders due to positional changes • Accessory renal arteries • Accessory renal veins • Pelvic kidneys • Horseshoe kidneys • Pancake kidneys
Bladder Anomalies • Urachal fistula • Urachal sinus • Urachal cyst • Exstrophy of bladder • Exstrophy of cloaca
Development of gonads • 4th week- primordial germ cells • 5th week – Gonadal ridge • 6th week – Incorporation of cells into gonadal cords • Upto 7th week – Indifferent gonad • Y- chrosomome- SRY gene for TDF in sex determining region of y ch. • Y chromosome has a testis determining effect on medulla of gonad • Type of gonad formed will further differentiate development of genital ducts and external genitalia
Development of gonad • Mesothelium- (of post. Abd. Wall) • Mesenchyme • Primordial germ cells- • large sperical cells among endoderm of yolk sac near allantois • Gonadal ridge- • mesothelial thickening on medial side of mesonephros + mesenchyme • Prim. Germ cells migrate along dorsal mesentery to gonadal ridge
Indifferent gonad Gonadal Ridge Gonadal cords (Fingerlike epithelial cords) Gonad consists of cortex & medulla xy xx Testis ovary
Testis • Condensation of cords • Extension into medulla • Branching & anastomoses-rete testis • Tunica albuginea develops • Connection of cords with surface nis lost • S. tubules, T recti & rete T • Mesenchyme- interstitial cells in 8th wk- hormones • S tubules remain solid till puberty
Hormones in male • 8-12 wk- peak of HCG --- Testosterone & androstenedion from Leydig cells • MIS / AMH from Sertoli cells
Mesonephric duct & tubules • Mesonephric tubules --- Efferent ductule + paradidymus in male • Epoophoron & paroophoron in female • M duct prox. Part --- duct of epididymus, appendix of epididymus • M duct distal part ---URETERIC BUD + ductus deferens, ejaculatory ducts & seminal gland • Appendix vesiculosa, duct of epoophoron & Gartner’s duct in female + URETERIC BUD
Descent of the Testis • The process vaginalis, (evagination of peritoneum), develops ventral to the gubernaculum and herniates through the abdominal wall along the path formed by the gubernaculum • The vaginal process carries extensions of the layers of the inguinal canal • In males these layers also form the coverings of the spermatic cord and testis • The opening in the transversalis fascia produced by the vaginal process becomes the deep inguinal ring • The opening created in the external oblique aponeurosis forms the superficial inguinal ring.
Descent of Testes • Enlargement of the testes • Atrophy of the mesonephroi • Atrophy of the paramesonephric ducts • Enlargement of the processus vaginalis • Enlargement of fetal pelvis • Trunk elongates • Androgens • Descend retroperitoneally • Gubernaculum • Increased intra abdominal pressure due to viscera • .
Development of Inguinal Canals • The inguinal canals form pathways for the testes to descend from the abdomen into the scrotum • Develop in both sexes because of the indifferent stage • As the mesonephros degenerates, a ligament – the gubernaculum – descends on each side of the abdomen from the inferior pole of the gonad • The gubernaculum passes obliquely through the developing anterior abdominal wall at the site of the future inguinal canal • The gubernaculum attaches caudally to the internal surface of the labioscrotal swellings (future halves of the scrotum or labia majora).