Introduction to Internet Worm
130 likes | 155 Vues
Introduction to Internet Worm. Cliff C. Zou CAP6133, Spring’08. Common forms of malware. “Malware” --- malicious software Viruses Worms Trojan horses Appear to be good but perform malicious actions Spyware, adware Email spam, phishing. What is an Internet worm?.

Introduction to Internet Worm
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Introduction to Internet Worm Cliff C. Zou CAP6133, Spring’08
Common forms of malware • “Malware” --- malicious software • Viruses • Worms • Trojan horses • Appear to be good but perform malicious actions • Spyware, adware • Email spam, phishing
What is an Internet worm? • A code that replicates itself over a computer network on its own and usually performs malicious actions • Exploit a vulnerability in some remote computers • OS, installed software has the vulnerability • Runs on compromised computers without permission from their users • Jump from one computer to another through the Internet • Automatic spreading without any human intervention • Basic difference from “viruses”
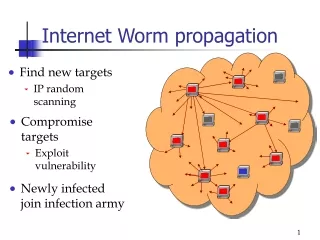
Worm propagation process • Find new targets • IP random scanning • Send TCP/SYN or UDP packet • Compromise targets • Exploit vulnerability Newly infected join infection army
Worm research motivation • Code Red (Jul. 2001) : 360,000 infected in 14 hours • Slammer (Jan. 2003) : 75,000 infected in 10minutesCongested parts of Internet (ATMs down…) • Blaster (Aug. 2003): 150,000 ~ 8 million infected DDOS attack (shut down domain windowsupdate.com) • Witty (Mar. 2004) : 12,000 infected in half an hourAttackvulnerabilityin ISS security products • Sasser (May 2004): 500,000 infected within two days Infection faster than human response !
How to defend against Internet worm attack? • Automaticresponse required • First, understanding worm behavior • Basis for worm detection/defense • Similar to epidemic spreading • Next, worm detection • Automatic (catch worm speed) • Unknown worm (no known signature) • Last, must have autonomous defense • False alarm? • More advanced worm? (e.g., polymorphic worm)
Internet Worm Modeling • Internet worm propagation is similar to epidemic spreading • Borrow models from epidemiology area • Modify models based on worm’s behaviors • Simple epidemic model: It: # of infected N: # of total population
# of increased infected in a unit time Prob. of a scan hitting vulnerable Simple worm propagation model W • address space, size W • N : total vulnerable • It : infected by time t • N-It vulnerable at time t • scan rate (per host), h
Worm modeling papers references • “How to own the Internet in your spear time” • First modeling paper after Code Red (most important paper) • “On the Performance of Internet Worm Scanning Strategies” • Modeling worm when it uses different scanning methods • “Models of Active Worm Defenses” • Modeling good worm defense against bad worm • ” Modeling the Spread of Active Worms” • Modeling based on discrete-time equations
Internet worm detection • Detection of unknown worm • No signature is known before a worm’s break out • Different forms of worm detection • Detect a worm’s breakout in the Internet • Minimum, does not provide further information • Detect infected hosts in the global Internet • Help filtering, protect local networks • Detect local infected hosts • Help maintenance; stop major damage before too late • Automatic signature generation • Most valuable; directly help worm filtering
Worm detection papers references • “Monitoring and Early Warning for Internet Worms” • “Fast Portscan Detection Using Sequential Hypothesis Testing” • “Cooperative Response Strategies for Large Scale Attack Mitigation” • “Automated Worm Fingerprinting” • Host-based, network traffic-based worm detection systems • Will be introduced in later topics
Internet worm defense • Can catch a worm’s rapid speed? • Automatic, quick enough • “Internet Quarantine: Requirements for Containing Self-Propagating Code” • Acceptable false alarm cost? • Major reason for slow deployment of automatic worm defense systems • People tend to forget worms until hit hard • “Throttling Viruses: Restricting Propagation to Defeat Mobile Malicious Code”
Advanced worms Polymorphic worms • A hot topic in current research community • Worm changes its code as it spreads out • Use encryption to hide code signature • Use code transformation technique for change • Make it harder to automatically generate signature • Two papers (attack/defense): • “Advanced Polymorphic Worms: Evading IDS by Blending in with Normal Traffic” • “Polygraph: Automatic Signature Generation for Polymorphic Worms”