Neuron
280 likes | 1.31k Vues
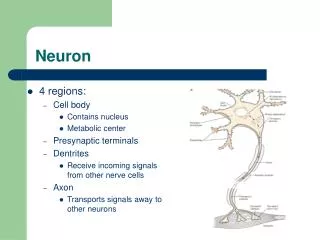
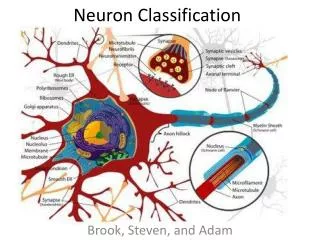
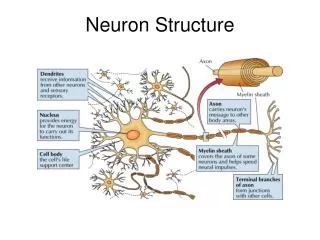
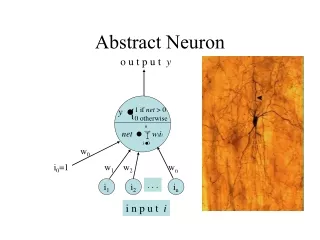
Neuron. 4 regions: Cell body Contains nucleus Metabolic center Presynaptic terminals Dentrites Receive incoming signals from other nerve cells Axon Transports signals away to other neurons. What is an Action Potential?. Defn. Electrical signal conveyed down an axon What causes it?

Neuron
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Neuron • 4 regions: • Cell body • Contains nucleus • Metabolic center • Presynaptic terminals • Dentrites • Receive incoming signals from other nerve cells • Axon • Transports signals away to other neurons
What is an Action Potential? • Defn. Electrical signal conveyed down an axon • What causes it? • An environmental stimulus (ex. Light, pressure, odor, mechanical contact, etc.) • These stimuli cause the axon hillock (start of the axon) to create an action potential • The action potential continues to the end of the axon
Action Potential Properties • Travel small or large distances (.1mm-3m) • Rapid and transient (duration of about 1ms) • Constant amplitude (100mV) • All or none nerve impulse • Travels in one direction (principle of dynamic polarization) (Dominos display)
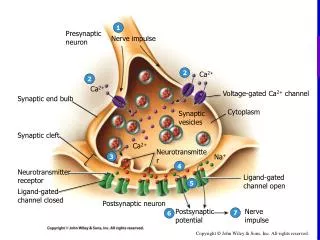
How does the action potential impact the neuromuscular junction?