NEURON CLASSIFICATION
180 likes | 486 Vues
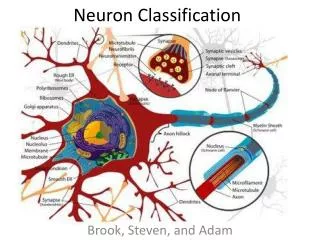
NEURON CLASSIFICATION. Presented by Deepa Challa Vijaya Lakshmi Boyina Bhavani Duggineni. INTRODUCTION. Neurons can be classified based on -Direction of travel - Neuron transmitter utilized - Electro physiological properties. INTELLIGENT THRESHOLDING.

NEURON CLASSIFICATION
E N D
Presentation Transcript
NEURON CLASSIFICATION Presented by DeepaChalla VijayaLakshmiBoyina BhavaniDuggineni
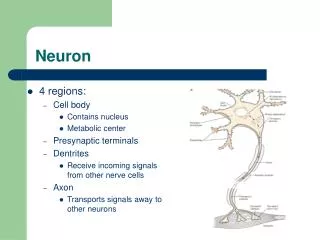
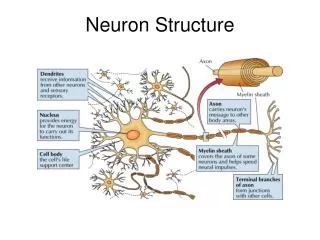
INTRODUCTION • Neurons can be classified based on -Direction of travel -Neuron transmitter utilized -Electro physiological properties
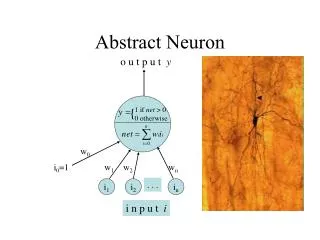
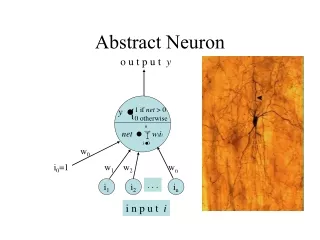
INTELLIGENT THRESHOLDING • This technique helps to improve the average accuracy of segmentation and makes the segmentation process more consistent • Involves three steps (1).Extracting features from sample images (2).Training the neuronal network (3). Testing with new images • Neuronal network means : In information technology, a neural network is a system of programs and data structures that approximates the operation of the human brain. Typically, a neural network is initially "trained" or fed large amounts of data and rules about data relationships
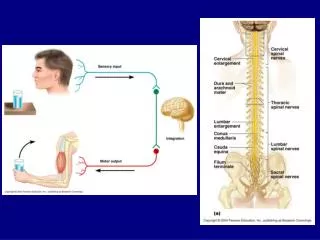
TRANSECTED SEGMENTS AND ADJACENT CELLS • Neurons can be transected in to segments, it helps in studying the specific parts of neuron by stripping the unnecessary regions. • Adjacent cells/neurons are the neurons that are located beside each other. These neurons communicates each other and separated by a space called synapse.
SEED POINTS • Seed point is a point against which information is tagged • Regional growing segmentation uses the concept of seed points • The initial region begins as the exact location of the seeds • Seed point selection is based on some user criterion
EXTENDABLE TO LARGER IMAGES AND STAINING INCONSISTENCIES • In imaging projects, the cells or specimen is focused under confocal or fluorescent microscope. The quality of images depends on staining of the cells and a proper staining enables us to produce good images for evaluation. • The software embedded in confocal microscope allows us to expand the images to larger size for analyzing
QUANTIFICATION OF NEURONS • Measurement of cell volume and surface area were made from a 3d confocal microscope image data set. • The Cavalieri principle was used to estimate the volume of the neuron, the surface area was estimated using the method of the spatial grid. • These new methods allow a detailed quantitative analysis of an Individual neuron that has also been characterized electro physiologicaly by current and/or voltage clamp recordings, which offers the unique possibility of directly correlating morphological data with the measured biophysical properties of the same cell.
2D V/S 3D SEGMENTATION • Segmentation can be done by various methods like regional growing, intelligent threshold etc. • 2D culture means sub culturing cells on sterile petridishes and 3D culture means culturing cells on matrigel and also provides the artificially created environment resemble the invivo. • Compared to 2D, 3D culture is more accurate and segmentation of neurons can be performed more precisely in 3D • 2D – Two dimensional • 3D – Three dimensional
References • Pampaloni, F., E. G. Reynaud, et al. (2007). "The third dimension bridges the gap between cell culture and live tissue." Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 8(10): 839-845.edi 3d culture • http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1058674183710165 • http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpl/abstractCitations.jsp?tp=&arnumber=295913&url=http%3A%2F%2Fieeexplore.ieee.org%2Fxpls%2Fabs_all.jsp%3Farnumber%3D295913 • http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Region_growing • http://www.irphouse.com/ijeee/ijeeev6n1_03.pdf