Projectile Motion
170 likes | 304 Vues
This document provides a comprehensive overview of projectile motion, detailing how objects move under the influence of gravity after an initial thrust. Key concepts include the independence of vertical and horizontal motion, and the formulas to calculate distance, velocity, and time for projectiles. Through examples such as a stone thrown from a cliff and a ball launched horizontally, it illustrates the fundamental principles of projectile motion. Learn how to apply these concepts to determine flight time, horizontal distance, and vertical speed upon impact.

Projectile Motion
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Projectile • An object that moves through the air only under the influence of gravity after an initial thrust • For simplicity, we’ll use 9.8 m/s2 for gravity. • Trajectory – path of a projectile
The vertical and horizontal components of a projectile are independent of each other • If 1 ball were dropped and another ball launched forward from the same height, they would hit the ground at the same time.
Video Break • Mythbusters
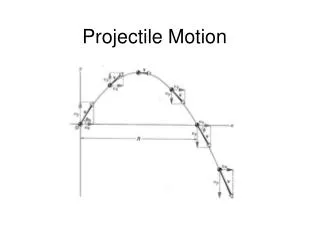
Force vectors for projectiles • Draw both horizontal and vertical vectors
VerticalHorizontal d = Vt V = d/t d = ½ gt2 V = gt
Vertical Component • Distance • d = Vit + ½ gt2 *Vi is 0, so it cancels! • d = ½ gt2 • Velocity • Vf = Vi + gt *Vi is 0, so it cancels! • V = gt
Horizontal Component • Distance • d = Vt • Velocity • V = d/t
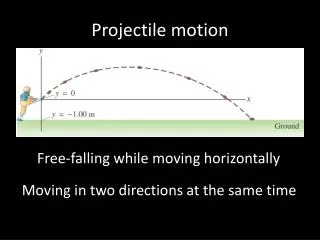
Example) A stone is thrown horizontally at 15 m/s from the top of a cliff 44 m high. • a) How long does it take to fall? • d = ½ gt2 • 44 = ½ (9.80)(t2) • 44 = 4.90( t2) • 8.9796 = t2 • t = 3.0 s 15m/s 44m
Example) A stone is thrown horizontally at 15 m/s from the top of a cliff 44 m high. • b) How far from the base of the cliff does it land? • d = Vt • d = (15)(3.0) • d = 45 m d
Example) A stone is thrown horizontally at 15 m/s from the top of a cliff 44 m high. • c) What is its vertical speed when it hits the ground? • V = gt • V = (9.80)(3.0) • V = 29.4 m/s
Example 2) A ball is thrown at a horizontal speed of 18 m/s. It’s flight time is 4.6 seconds. • How high does the ball go? • d = ½ gt2 • d = ½ (9.80)(2.32) • d = 25.92 m
Example 2) A ball is thrown at a speed of 18 m/s. It rises and falls in 4.6 seconds. • How far away does it land? • d = Vt • d = (18)(4.6) • d = 82.8 m
Example 2) A ball is thrown at a speed of 18 m/s. It rises and falls in 4.6 seconds. • What is its vertical speed when it hits the ground? • V = gt • V = (9.8)(2.3) • V = 22.54 m/s