Organic Chemistry Introduction
240 likes | 516 Vues
Organic Chemistry Introduction. Topic 10.1.9 – 10.1.13. Compounds up to 6 carbon atoms with functional groups (10.1.9). Compounds up to 6 carbon atoms with functional groups (10.1.9-10). Know these 7, only have to recognize the 3 in the. Alcohols: suffix = “anol”. propan-1-ol.

Organic Chemistry Introduction
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Organic Chemistry Introduction Topic 10.1.9 – 10.1.13
Compounds up to 6 carbon atoms with functional groups (10.1.9)
Compounds up to 6 carbon atoms with functional groups (10.1.9-10)
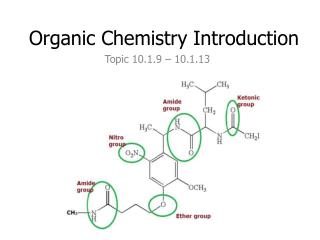
Alcohols: suffix = “anol” propan-1-ol propan-2-ol 2-methyl propan-2-ol
Aldehydes: suffix = “anal” propanal Note: an aldeyhde group is always on an end carbon so don’t need a number butandianal
Ketones: suffix = “anone” propanone (don’t need C#, must be in between two carbons) butanone (don’t need C#, must be in between two carbons) 2-pentanone or penta-2-one
butandione pentan-3-one
Carboxylic Acids: suffix = “anoic acid” butanoic acid Note: a carboxyl is always on an end carbon propandioic acid
Halides: prefixes = “fluoro, chloro, bromo, iodo” 1-bromopropane 2-chlorobutane 1,2-diiodoethane 1,2-difluoroethene 1,2-difluoroethene 1,1,2-trifluorothene
Only identify the following functional groups in structures: (10.1.11)
with reference to the carbon that is directly bonded to an alcohol group or a halogen: Primary = carbon atom is only bonded to one other carbon Secondary = carbon atom is bonded to two other carbons Tertiary = carbon atom is bonded to three other carbons 10.1.12 Identify primary, secondary and tertiary carbon atoms in alcohols (-OH) and halogenoalkanes (-F, -Cl, -Br, -I)
Volatility: how easily a substance turns into a gas the weaker the intermolecular force, the more volatile it is from strongest to weakest ionic › hydrogen bonding › dipole-dipole › van der Wall’s therefore volatility… alkane (only Van der Wall’s) › halogenoalkane › aldehyde › ketone › amine › alcohol (H bonding) › carboxylic acid (H bonding) 10.1.13 Discuss the volatility and solubility in water of compounds containing the functional groups listed in10.1.9.
Solubility: a solute’s ability to dissolve in a polar solvent (water) the more polar a substance is, the more soluble it is solubility decreases as chain length increases smaller alcohols, aldehydes, ketones & carboxylic acids are typically soluble they are all polar as is water