Temperature and Heat
120 likes | 140 Vues
Learn about temperature, heat transfer, thermal energy, and how objects reach thermal equilibrium. Discover conduction, convection, and radiation examples explained in simple terms.

Temperature and Heat
E N D
Presentation Transcript
When a doctor listens to your heart, what is it about the stethoscope that makes it feel cold? • When you first sit down in a desk, why does the seat feel cold? The answer has to do with how thermal energy is transferred!
You think of the words temperature and heat as having to do with things that feel hot. But they also have to do with things that feel cold—such as the stethoscope. • Temperature - measure of average kinetic energy of particles in an object • Heat - thermal energy transferred between objects at different temperatures
When two objects at different temperatures come into contact, the object with the higher temperature transfers thermal energy to the object with the lower temperature. Example: The doctor's stethoscope touches your back. Energy is transferred from your back to the stethoscope because your back has a higher temperature than the stethoscope. This energy is transferred quickly, so the stethoscope feels cold to you.
Heat and Thermal Energy • Heat is thermal energy being transferred. • Thermal energy is the total kinetic energy of the particles that make up a substance. Thermal energy is measured in joules (J).
Something at a high temperature has more thermal energy than it would have at a lower temperature. • Thermal energy also depends on how much of a substance there is. Example: Although both soups are at the same temp, there is more soup in the pan. So, the soup in the pan has more thermal energy than the soup in the bowl.
Reaching the Same Temperature • When objects that have different temperatures come into contact, energy will always be transferred. • Energy passes from the warmer object to the cooler object until both have the same temperature.
The point at which two objects that are touching reach the same temperature is called thermal equilibrium.
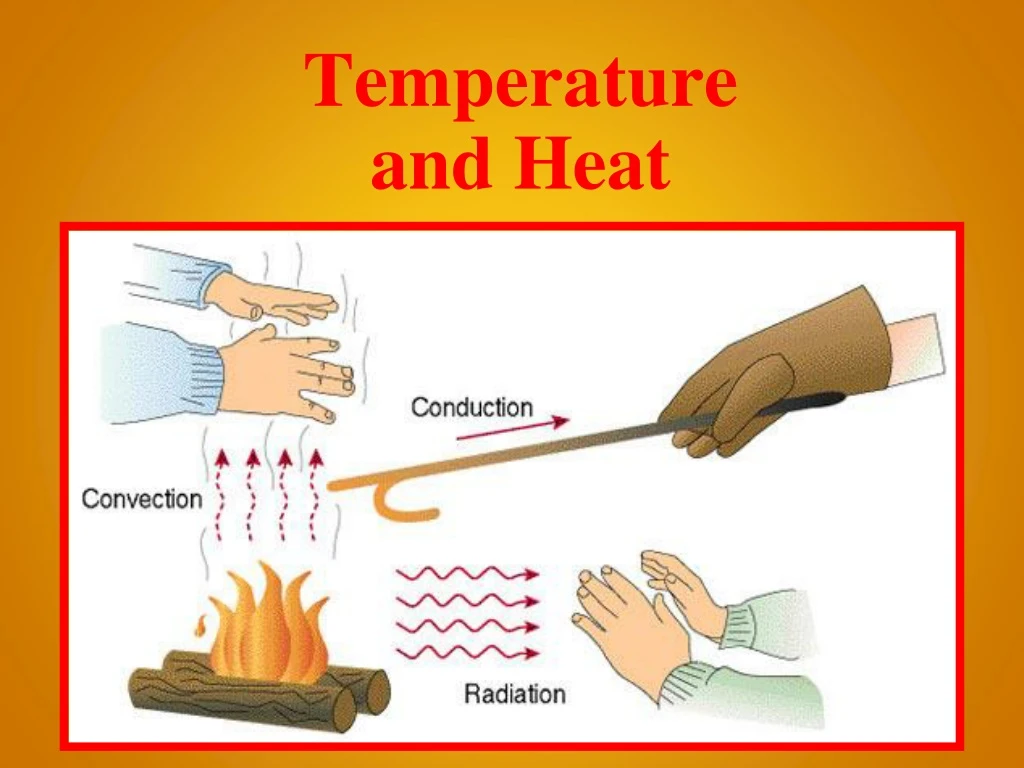
Conduction • Heat moves through a solid by conduction. • The motion of particles in the hot part of the solid transfer their energy to nearby ones. • Ex: touching a hot stove
Convection • Heat moves through liquids or gases by convection. • Hot fluids move upward while cooler fluids sink. • Heat is transferred in a continuous convection current. Ex: boiling water • This is also how wind is created in our atmosphere!
Radiation • Heat can travel in the form of electromagnetic radiation. • It does not require touching of molecules. • The most common form is thermal or infrared radiation. Ex: the sun