Understanding Photosynthesis: The Process of Light-Driven Energy Creation
60 likes | 187 Vues
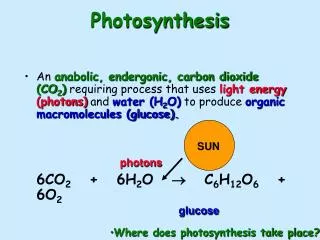
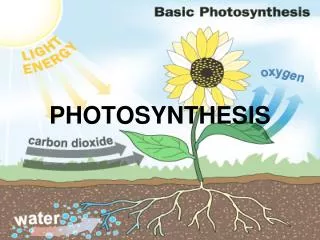
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants use light to create energy. Key elements include chlorophyll, carbon dioxide from the air, solar energy, and water. The process begins when chlorophyll captures sunlight, while carbon dioxide enters through stomata. Water from roots combines with carbon dioxide to form simple sugars, which are stored as starch and transformed into fats and proteins. The end products travel through the phloem, aiding plant growth, while oxygen and water vapor are released through the stomata, completing the cycle.

Understanding Photosynthesis: The Process of Light-Driven Energy Creation
E N D
Presentation Transcript
PHOTOSYNTHESIS “To make something with light”
Required elements • Chlorophyll • Carbon dioxide from air • Solar energy • water
Steps for photosynthesis • Chlorophyll traps sunlight to use as energy. • Carbon dioxide enters through the stomata. • Water brought from the roots through the xylem reacts with CO2. • Reaction forms a simple sugar. • Sugar is stored as starch, used for energy and converted to fats and proteins.
Steps continued 6. The products travel to the rest of the plant through the phloem to help it grow and stay healthy. • Oxygen is produced in the reaction and water vapor. • Stomata releases the oxygen and water.