The Structure of DNA
180 likes | 413 Vues
The Structure of DNA. An example of scientists building upon each others discoveries. Where is hereditary information stored in the cell?. Joachim Hammerling studied the unicellular green algae, Acetabularia.

The Structure of DNA
E N D
Presentation Transcript
The Structure of DNA An example of scientists building upon each others discoveries
Where is hereditary information stored in the cell? • Joachim Hammerling studied the unicellular green algae, Acetabularia
Hammerling’s Conclusion: Hereditary information in Acetabularia is stored in the foot of the cell, where the nucleus resides.
Can Hereditary Information Pass between Organisms? Fredrick Griffith’s experiments in 1928
Griffith concluded that hereditary information can pass from dead cells to living cells, transforming them. He called this transformation, a change in genotype and phenotype due to assimilation of foreign DNA.
What Is the Genetic Material: Proteins or DNA • What is the “agent” responsible for transforming the bacteria in Griffith’s experiment? • The predominant idea was that proteins were the genetic material
“The Avery Experiments”—What is the “Transforming Molecule?” Avery and his colleagues purified various molecules from heat-killed pathogenic bacteria & tried to transform live bacteria with each type
The Transforming Principle is DNA • Avery, MacLeod & McCarty observed that only DNA was able to transform the harmless bacteria into pathogenic ones. • Conclusion: DNA is the transforming agent • Their results were met with skepticism
Hershey & Chase Experiment, 1952Conclusion: DNA, not protein, is the hereditary material
Chargaff’s Experiments, 1947 In the next 10 minutes, you will simulate Chargaff’s 1947 experiments using images of the nucleotide bases from different species.
Chargaff’s Rules, 1947 • In any species there is an equal amount of Adenine and Thymine bases and an equal amount of Guanine and Cytosine bases
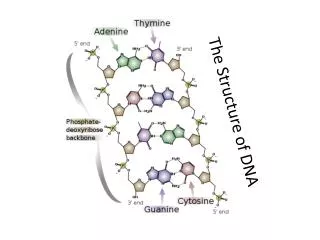
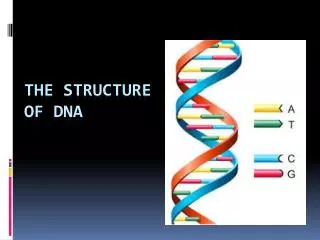
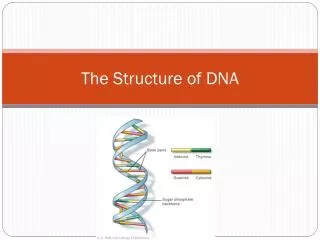
Complementary Base Pairing in DNA A & T are paired, they form two hydrogen bonds G & C are paired, they form three hydrogen bonds
What is the structure of DNA? • Rosalind Franklin performed x-ray diffraction experiments on DNA in 1953 • She concluded that DNA had the shape of a helix, a diameter of 2 nanometers and a completed helical turn every 3.4 nanometers
Aha! • In 1953, James Watson (age 23) and Francis Crick (age 43) used Rosalind Franklin’s results to determine the structure of DNA
Nobel Prize, 1962 • Wilkins, Crick & Watson receive the Nobel Prize for the discovery of the structure of DNA.