XML Parsers
290 likes | 660 Vues
XML Parsers. Kanda Runapongsa ( krunapon@kku.ac.th ) Dept. of Computer Engineering Khon Kaen University. What are XML Parsers?. In order to process XML data, every program or server process needs an XML parser The parser extracts the actual data out of the textual representation

XML Parsers
E N D
Presentation Transcript
XML Parsers Kanda Runapongsa (krunapon@kku.ac.th) Dept. of Computer Engineering Khon Kaen University
What are XML Parsers? • In order to process XML data, every program or server process needs an XML parser • The parser extracts the actual data out of the textual representation • It is essential for the automatic processing of XML documents 168493: XML and Web Services (II/2546)
What are XML Parsers? (Cont.) • Parsers also check whether documents conform to the XML standard and have a correct structure • There are two types of XML parsers • Validating: check documents against a DTD or an XML Schema • Non-validating: do not check documents against a DTD or an XML Schema. 168493: XML and Web Services (II/2546)
Available XML Parsers • MSXML: Microsoft XML Parser: http://msdn.microsoft.com/xml/ • Apache Xerces: XML parsers in Java and C++: http://xml.apache.org • IBM AlphaWorks: http://www.alphaworks.ibm.com/tech/xml4j • expat: http://www.jclark.com/xml/expat.html • XP: http://www.jclark.com/xml/xp/ • Other sources • XML.com web site • Cover Pages: XML web site 168493: XML and Web Services (II/2546)
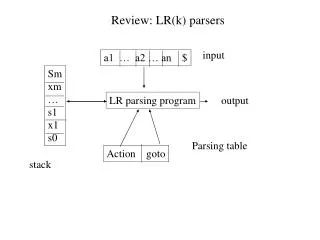
SAX and DOM • SAX (Simple API for XML) and DOM (Document Object Model) allow programmers to access their information stored in XML documents • Using any programming language and a parser for that language • Both of them take very different approaches to giving you access to your information 168493: XML and Web Services (II/2546)
What is DOM? • DOM gives you access to the information stored in your XML document as a hierarchical object model • DOM creates a tree of nodes (based on the structure and information in your XML document) • You can access your information by interacting with this tree of nodes 168493: XML and Web Services (II/2546)
Hierarchical Structure 168493: XML and Web Services (II/2546)
DOM • Each element node actually contains a list of other nodes as its children • These children might contain text values or other nodes • DOM preserves the sequence of the elements that it reads from XML documents 168493: XML and Web Services (II/2546)
What is SAX? • SAX chooses to give you access to the information in your XML document, not as a tree of nodes, but as a sequence of events • SAX chooses not to create a default object model on top of your XML document (like DOM does) 168493: XML and Web Services (II/2546)
SAX vs. DOM • In the case of DOM, the parser does almost everything • Read the XML document in • Create an Object model on top of it • Give you a reference to this object model (a Document object) so that you can manipulate it • SAX doesn’t expect the parser to do much 168493: XML and Web Services (II/2546)
SAX vs. DOM (Cont.) • For SAX, the parser should • Read in the XML document • Fire a bunch of events depending on what tags it encounters in the XML document • Then, the programmer needs to make sense of all the tag events and create objects in their own object model 168493: XML and Web Services (II/2546)
SAX vs. DOM (Cont.) • SAX can be really fast at runtime if your object model is simple • It is faster than DOM because it bypasses the creation of a tree based object model of your information • On the other hand, you have to write a SAX document handler to interpret all the SAX events 168493: XML and Web Services (II/2546)
SAX Events • SAX events can be • An event for every open tag • An event for every close tag • An event for #PCDATA section • An event for CDATA section • Your handlers have to interpret these events and make sense out of them 168493: XML and Web Services (II/2546)
When to Use DOM • DOM is quite easy to implement • Good for the development to be done in a short amount of time • DOM has crated a tree of nodes • When you need to quickly access children and parent of current nodes • When you need to modify an XML structure • What are the disadvantages of using DOM? 168493: XML and Web Services (II/2546)
When to Use SAX • SAX requires little memory because • It does not construct an internal representation of the XML data • It works well when you simply want to read data and have the application act on it • You see the data as it streams in, but you can’t go back to an earlier position or leap ahead to a different position 168493: XML and Web Services (II/2546)