Functional Information from Genetic Interactions
230 likes | 348 Vues
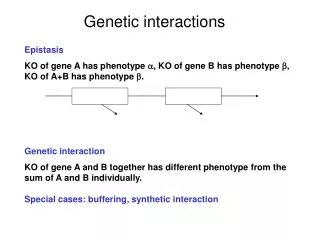
Functional Information from Genetic Interactions . Bernd Fischer. Genome Wide Association Studies. Currently ~400 variants that contribute to common traits and diseases are known Individual and the cumulative effects are disappointingly small

Functional Information from Genetic Interactions
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Functional Informationfrom Genetic Interactions Bernd Fischer
Genome Wide Association Studies • Currently ~400 variants that contribute to common traits and diseases are known • Individual and the cumulative effects are disappointingly small • Limitations to current genome-wide association studies: • Common SNPs miss rare variants with potentially huge effects • Many structural variants undetected, since not covered by SNP-arrays • Common variants with low penetrance also missed • Higher order effects are hard to estimate, due to combinatorial explosion • Epistasis may confound identification In this talk: Detection of Pairwise Interactions by Combinatorial RNAi knock-downs
Design of Combinatorial knock-down Screen • Subset of 93 Drosophila kinases and phosphatases • each targeted by two independent dsRNA designs • validation of knock-down by qPCR • 96 plates (~37.000 wells) • 4.600 distinct gene pairs
Imaging • Cells grow for 5 days (Dmel2 cell line) • Fixate and stain with Hoechst (DNA content) • Image with Cytometry laser scanner (TTP LabTech Acumen Explorer) Joint Work with Thomas Horn, Thomas Sandmann, Michael Boutros, DKFZ
Image Processing B = conv. with ring Input image A = conv. with Gaussian A > B + epsilon Label image (cell area) Detected Cells
Phenotypic Effects of Single Knock Downs #cells area
Screen Plot of Read-out (Number of Cells) within screen replicates (cor=0.968) independent daRNA designs (cor=0.902) between screen replicates (cor=0.948)
Estimating Genetic Interactions • For many phenotypes, the main effects (single gene) are multiplicative for non interacting genes i, j: • Additive on logarithmic scale • Estimation of main effects (assume that interactions are rare) • Detect Genetic Interactions: Compare to (t-test) effect of control main effect of dsRNA j error term interaction term 0, for non interacting genes ≠0, for interacting genes measurement (nr cells, growth rate, …) main effect of dsRNA i 26/10/2014
Screen Plot of Interaction Score (#cells) within screen replicates (cor=0.968) independent daRNA designs (cor=0.902) between screen replicates (cor=0.948)
Interaction Surfaces viability interactions area interactions
Interaction Surfaces of Ras85D Ras85D CG42327 Ras85D Gap1 Ras85D drk Ras85D Ras85D no interaction pos. interaction strength, presence, and direction of interaction depends on knock-down level genes with neg. phenotype show pos. self-self interactions
Overview of Genetic Interactions • non-redundent interactions between features • interactions overlap significantly with known genetic interactions • overlap with human interologs (their human orthologs interact) • significant overlap even for feature specific interactions • interactions can change direction (pos. in nrOfCells, neg. in area)
Epistatis of Gap1 Interactions of Gap1 Interactions of PTP-ER single knock-down level of second knock-down single knock-down level of second knock-down The viability effect of most genes is recovered, if Gap1 is knocked down in addition
Clustering of Interaction Map RasMAPK-pathway JNK-pathway
Classification cross-validation functional prediction of new genes cross-validated posterior probabilities of the classifier are shown
In vitro and in vivo validation of Cka effect on downstream genes and phospho-ERK Cka binds to STRN-complex Cka-knockdown shows typical in vivo RASMAPK phenotype
Image processing, Segmentation Segmentation of nuclei Segmentation of cell body
Automatic Classification of Cell Morphology inter-phase pro-phase prometa-ph. meta-phase ana-phase telo-phase cytokinesis dead cells binucleated
Modeling Genetic Interactions • define models • for genetic • interactions for • each feature • joint estimation • of interaction • from high dim. • feature vector • predict gene • function from • interaction data • estimate causal • relationships • between genes • (network learning) whole image features (texture) features derived from segmented cells: nrCells, mean area, mean intensity, mean texture, mean shape automatic morphology classification: mitotic stage histogram (count data)
Current Work • Large-scale genetic interaction screen in Dmel2-cells • ~1500 chromatin-related genes x 100 query genes • full microscopic readout (4x and 20x magnification) • 3 channels DAPI (staining chromatin, nucleus marker) H3p (staining histone phosphorylations, mitosis marker) aTubulin (spindle phenotypes)