BREAST CANCER
1.27k likes | 1.53k Vues
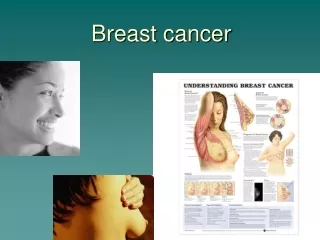
BREAST CANCER. The Breast. A ducts B lobules C dilated section of duct to hold milk D nipple E fat F pectoralis major muscle G chest wall/rib cage Enlargement: A normal duct cells B basement membrane C lumen (center of duct). Breast Carcinoma Incidence.

BREAST CANCER
E N D
Presentation Transcript
The Breast • A ducts • B lobules • C dilated section of duct to hold milk • D nipple • E fat • F pectoralis major muscle • G chest wall/rib cage • Enlargement: • A normal duct cells • B basement membrane • C lumen (center of duct)
Breast Carcinoma Incidence • 20% of all cancers in women • Commonest cause of death - 35-55y • In UK 1 in 10-12 chances • 1 in 8 women in US • Less incidence in Asia • Majority of cancers arise in the ducts. • Very rare before age 25
Risk Factors: • Female sex..!, Age, Obesity, high fat diet • Maternal relative with breast cancer. • Longer reproductive span. • Nulliparity, Oral contraceptives • Later age at first pregnancy. • Atypical epithelial hyperplasia. • Previous breast cancer/Endometrial Ca. • Geographic factors - country • BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes
Breast Cancer Risk Factorsthat cannot be changed Age GENDER - All women are at risk Reproductive History Family/Personal History Menstrual History Race Radiation Treatment with DES Genetic Factors
Breast Cancer Risk Factorsthat can be controlled Obesity Obesity All women are at risk All women are at risk Not having children Not having children Exercise Exercise Breastfeeding Breastfeeding Birth Control Pills Birth Control Pills Hormone Replacement Therapy Hormone Replacement Therapy Alcohol Alcohol
Pathology ( WHO classification) • Epithelial (mammary tissue) • Non invasive • DCIS • LCIS • Invasive • Ductal 85 % • Lobular 9 % • Mucinous 5 % • Papillary < 5 % • Medullary < 5 % • Mixed Ct & epithelial • Miscellaneous • Paget’s disease • IBC
Pathology (Foot& Stewart classification) • Neoplasm of mammary tissue proper • Neoplasm of lobular epithelium 9- 10 % • LCIS 50 % • Lobular carcinoma invasive 50 % • Neoplasm of ductal epithelium 85 % • DCIS • Ductal carcinoma Invasive ( IDC) • NOS ( simple type) • Special types ( scirrhous, medullary, mucinous, papillary, cribriform, comedo, tubular, secretory with metaplasia) • Unusual presentations • Paget’s disease • IBC
Pathology (Foot& Stewart classification) • Malignant mesenchymal neoplasm • Sarcoma • Lymphomas • Myeloid leukemia • Miscellaneous malignancies • Skin • SCC • BCC • Skin adenxa ( carcinoma of sweat glands or sebaceous glands) • Undifferentiated carcinoma • Metastatic • Female ( other breast, lung, MM) • Male (prostate)
Carcinoma in situ It is a spectrum of pre invasive neoplastic changes in the breast includes; • DCIS 4 % symptomatic 25 % screen detected • LCIS <1 % symptomatic 1% screen detected • Hyper plastic appearance ( ductal or lobular)
Ductal Carcinoma in Situ • It is the group of neoplasm arising from ductal epithelium & confined by basement membrane • Ducts expanded by large irregular cells with lage irregular nuclei • Malignant cells are confined by basement membrane
Ductal Carcinoma in Situ (classification) • Comedo DCIS • High grade cytology • Extensive necrosis • Branched calcification • Non Comedo DCIS • Low grade cytology • Lack necrosis • Lack calcification • Cribribriform • Solid • micropapillary Intermediate histology
Ductal Carcinoma in Situ • Clinical presentation • Asymptomatic > 50 % in screening programs as abnormal mamographic finding • Nipple discharge • Paget’s disease • Risk of invasive BC is 40 % over 30 y • Multicentricity in 50 %
Ductal Carcinoma in Situ(Diagnosis) • Sterotactic CNB • U/S guided CNB • Wire or ink guided excisional biopsy which is a must if; • Atypical ductal hyperplasia • Radial scar • Non specific diagnosis • Lack correlation with mammogram • Wedge biopsy if paget’s
Ductal Carcinoma in Situ(Treatment) Depend on Van Nuys Prognostic Index which classify patients into 3 groups Depending on 3 factors 3- Surgical free margin 1- Tumor size 2- Histological grade Intermediate risk Low risk High risk Wide local excision (BCS) BCS & irradiation Mastectomy SSM
Lobular Carcinoma In Situ • It constitute 25 % of CIS • The risk of invasive cancer is 20 – 30 % life time and bilateral • It is multicentric in 80 % • Never palpable mass • Treatment • Follow up by • C/E every 4 months • Mammography yearly • Chemoprevention by Tamoxafen or raloxifene • Mastectomy which is rarely used
Invasive Breast Cancer • Epithelial Invasive BC • Ductal 85 % • Lobular 9 % • Mucinous 5 % • Papillary < 5 % • Medullary < 5 % • Mixed Ct & epithelial • Miscellaneous • Paget’s disease • IBC
Infiltrating Duct Carcinoma: small hard (Atrophic scirrhous) • 5 % • post menopausal with shriveled breast • NEA • Small size • Irregular in shape • Very hard in consistency • MP • ++++ FT • + islads of malignant spheroidal cells • Infrequant mititic figures • Very slowly progress 10 Y • Very late metastases • Best prognosis
Infiltrating Duct Carcinoma: Fibrosis(Scirrhous) • 75 % • Middle aged 40 – 60 Y • NEA • Small size • Irregular in shape • hard in consistency • MP • +++ FT • ++ scanty as finger like processes • slowly progress • late metastases • Good prognosis
Medullary Carcinoma: Large soft • 3- 5 % • Well developed breast of young woman • NEA • Largr fleshy in size • Brain like cut section in shape with hge & necrosis • Soft in consistency • MP • ++ delicate FT • ++ + highly malignant cells • Rapidly progress • Moderate metastases • Good prognosis • Rapid increase lead to early presentation • Fungate more than infilttrate • Late LN affection dt large cell size
Mucoid or Colloid Carcinoma • It form a bulky mass with mucoid degeneration & necrosis • It grow slowly & disseminate late & may reach huge sizes so have good prognosis after surgery • Signet ring shaped cells dt mucoid materials
Lobular Carcinoma • It constitute 9 % • Arise in the terminal lobules • It could take different presentation as ductal carcinoma
Paget’s Disease • It is a chronic eczematoid malignant eruption of the nipple • 1 % in middle aged and old woman • Etiology • Old theory ( skin tumor with secondary breast mass • New theory ( tumor in terminal ducts as in situ cancer then spread • Outward to nipple and skin • Inward breast mass
Paget’s Disease • Hyper plastic changes in all layers of epidermis (epidermal hypertrophy) • Characteristic paget’s cells • Large vaculated cells • Deeply stained eccentric nucleus • Subdermal round cell infiltration
Paget’s Disease( Clinical picture) • Persistent eczema like condition that affect old female 50 Y which does not respond to topical treatment • Unilateral erosion of the nipple which is red, thick, scaly & crusted without vesicles or itching • Serosangious discharge • Mass in the breast in 2 Years
Paget’s Menopause Unilateral No vesicles or itching Sub areolar mass after 2 years Not respond to topical treatment Biopsy paget cells Eczema Lactation Bilateral Vesicles and itching No mass Respond to topical treatment No paget cells
Paget’s DiseaseDiagnosis • Mammography is a must • Detect sub clinical mass • Detect micro calcification • Detect multi centricity • Biopsy ( full thickness nipple biopsy)is diagnostic where there are 3 different types • Paget’s disease with DCIS ( high grade comedo) • Paget’s disease with invasive cancer ( commonest) • Paget’s disease confined to epidermis of nipple & areola ( rarest)
Paget’s Disease( Treatment) • The standard treatment is mastectomy • Recently BCS is used with segmentectomy of nipple & areola & radiotherapy Paget’s disease with no mass Or with DCIS Paget’s disease with mass or with invasive cancer Segmentectomy Of N & A & Axillary dissection Segmentectomy Of N & A + Ve margins multicentric • Ve margins • No multicentric Radiotherapy Mastectomy
Paget’s Disease( Treatment) Use of chemotherapy based on 5 prognostic indication of chemotherapy • Age < 35 year • Tumor > 1 cm • Tumor high grade • + ve LN • - ve ER
IBC( Inflammatory breast cancer • Very rare • Well developed breast of young woman during pregnancy and lactation should be DD of abscess • NEA • Diffuse swollen, hot on palpation ,with dilated vein • Soft in consistency • MP • + very little FT • ++ + + highly malignant anaplastic cells • Rapidly progress • Very early metastases • Bad prognosis
IBC( Inflammatory breast cancer • It is very similar to acute breast abscess with the following differences • It is a diffuse lesion • No pyrexia • LN not tender • Progressive in nature • No lecucytosis • No respond to antibiotic
Spread of Breast Carcinoma: • Methods of spread • Direct • Lymphatic • Blood • Trans- celomic • Theories of spread • Loco-regional theory • Systemic theory
Tumor TNM Staging • Tx primary tumor can not be assessed • Tis In situ carcinoma & paget’s disease • T0 no palpable mass • T1 tumor < or = 2 cm • T1a < or = 0.5 cm no deep fixation • T2b 0.5 – 1 cm + deep fixation • T3c 1 – 2 cm + deep fixation • T2 tumor 2 – 5 cm • T2a no deep fixation • T2b deep fixation • T3 tumor 5 – 10 cm • T3a no deep fixation • T3b deep fixation • T4 tumor of any size • T4a direct chest extension • T4b skin ( Peau d’orange, skin nodule & ulceration) • T4c T 4a + T4b • T4d inflammatory breast cnacer
TNM Staging Nodes • N x can not be assessed • N 0 not palpable LN • N 1 palpable homo-lateral axillary LN and mobile • N 2 palpable homo-lateral axillary LN and fixed • N 3 ipsilateral internal mammary LN • MXcan not be assessed • M 0 no known metastases • M 1 distant metastases including supra-clavicular LN Metastases
TNM staging Stage I T1 N0 M0 Stage II a T1 N1, T2 N0, T0 N1 Stage II b T2 N1, T3 N0
TNM staging Stage III a any N2 any T3 except T3 N0 Stage III b any N3 any T4
Stag Definition 5-year Surv (%) 7-year Surv (%) I Tumor 2 cm or less without spread 96 92 II Tumor 2-5cm with regional lymph node involvement but without distant metastases, OR > 5 cm in diameter without spread 81 71 III Any size with skin/chest wall fixation, & axillary or internal mammary nodal involvement, without distant metastases 52 39 IV Tumor of any size with or without regional spread but with evidence of distant metastases 18 11
Manchester classification • Stage I ( 85%) • Mobile tumor • Free axilla • Paget’s • Stage II ( 66 %) • Mobile tumor • Mobile axillary LN • Stage III ( 41 %) • Tumor fixed • LN fixed • Stage IV ( 10%) • Wide dissemination • suprac;lavicular LN
Prognosis • Clinical factors • Age • Sex • Site • Stage • Grade • Pregnancy • Pathological factors • Tumor type • Grade • Axillary LN • Biological factors • Receptors ER, Pg R • Tumor markers • DNA ploidy • S phase fraction
Nottingham Prognostic Index (NPI) • Axillary LN involvement • 1 no node • 2 1-3 node • 3 4 or more node • Grade (1, 2, 3) • Tumor size in cm x 0.2