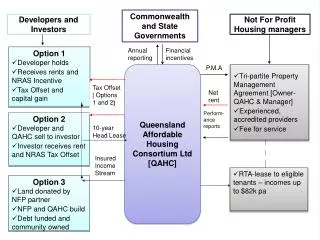
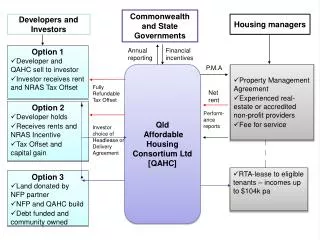
System Users and Developers
240 likes | 272 Vues
Explore the roles of information specialists, system analysts, programmers, and more within IS organizations. Learn about IS organizational structures and end-user computing benefits, risks, and education criteria.

System Users and Developers
E N D
Presentation Transcript
System Users and Developers Source: Management Information System McLeod & Schell
Information Services (IS) Organization • Information Services • Unit of the firm that has responsibility for the majority of the information resources • Other names: MIS Division, MIS Dept or IT Dept • Information resources • Hardware, software, information specialist, users, facilities, database & information • Information resources located in the IS and are the responsibility of the Chief Information Officer (CIO) • Information specialists • Person whose full-time responsibility is to contribute to the availability of information resources in the firm
Information Services (IS) Organization • Information specialists • System analysts • Programmers • Operators • Database administrators • Webmasters • Network specialists
Information Specialist • System Analysts • Work with the users to develop new systems & improve existing systems • Expert at defining problems & in preparing written documentation on how the computer will assist in solving the problems • Programmers • Use the documentation prepared by the system analysts to code computer programs that transform the data into information that is needed by the user. • Some firms combine the functions of the system analyst & programmer to be programmer analyst
Information Specialist • Operators • Run the large-scale computing equipment (such as: mainframe & server) • Monitor the consoles, change paper form in the printers, manage library of tape & storage, etc • Database Administrator • Has responsibility for the firm’s database • Planning, Implementation, Operation & Security
Information Specialist • Network Specialist • Work with system analyst and users in establishing the data communication networks that tie together widespread computing resources. • Expertise in the fields of computing & telecommunication • Webmaster • Responsible for the content & presentation of the firm’s website • Work with network specialist to ensure that the communication network between the firm, customers & business partners is always open • To track people who come to the firm’s website, an information to be used to review website’s effectiveness
IS Organizational Structure • Centralized structure CIO Manager System Development Manager System Maintenance Manager Computer Operation Manager Database Administrator Network Manager System Analyst System Analyst Operation Personnel Database Admin Network Specialist Programmer Programmer
IS Organizational Structure • Trend from centralized to decentralized structure. • Allocating information resources to the business unit & granting the units the authority to decide how the resources would be applied • Divisional information officer (DIO)
IS Organization Structure • Innovative Organizational Structures • Partner model • IS works with business area in using IT to achieve business innovation • Platform model • IS not active initiate business innovation, but provide the IT resources so that innovation can be accomplished in business area • Scalable model • IS should provide information resources based on market opportunities
Network Model of Information System Organization Top Management Visioning Network Innovation Network Sourcing Network CIO Business Area Vendors
Network Model (Cont’d) • Visioning network enables the CIO to work with top mgmt. in strategic planning for information resources. • Innovation network is used by the CIO to interface with business areas so that innovations can be developed. • Sourcing network is utilized to interface with vendor for acquiring information resources.
End-user Computing • Traditional Communication Chain Database Admin Computer User System Analyst Programmer Operator Network Specialist Webmaster
End-user Computing • End-user computing (EUC) is the development by users of all or parts of their information systems. • EUC has 4 main influences: • The impact of computer education. • The information services backlog. • Low-cost hardware. • Prewritten software.
End User Computing Communication Chain Information Specialist support User Computer communication
Benefits of EUC • Match capabilities and challenges. • The shift in the workload for system development to user area frees up the information specialist to concentrate on organization-wide complex system • Reduce the communication gap. • User understand the problem area better than technology • Information specialist less knowledgeable in the problem area
Risks of EUC • Poorly targeted systems. • Poorly designed & documented systems. • Inefficient use of information resources. • Loss of data integrity. • Loss of security. • Loss of control.
Education Criteria, Knowledge, & Skills Needed for IS Careers • Systems development knowledge • Computer literacy • Information literacy • Business fundamentals • Systems theory • Systems development process • Systems life cycle (SLC) & Systems development life cycle (SDLC) • Systems modeling
Education Criteria, …(Cont’d) • Systems development skills • Communications skills • Analytical ability • Creativity • Leadership
Managing the Knowledge • Office automation includes all of the formal & informal electronic systems primarily concerned with the communication of information to and from persons both inside and outside the firm. • Example: word processing, spreadsheet, e-mail, e-calendar, videoconference, etc • Shift from clerical to managerial problem solving.
Virtual Office • Office work can be done at virtually any geographical location as long as the work site is linked to one or more of the firm’s fixed location by some type of e-communication capability • Telecommuting describes how employees could electronically “commute” to work. • Hoteling is when the firm provides a central facility that can be shared by employees as the need for office space and support arises.
Virtual Office (Cont’d) • Advantages • Reduced facility cost. • Reduced equipment cost. • Reduced work stoppages. • Social contribution. • Disadvantages • Low morale. • Fear of security risks.
Virtual Organization • Three I Economy is those industries that are most attracted to the concept of the virtual office & the virtual organization and those that add value in the form of information, ideas, and intelligence. • Eg: Education, health care, entertainment, travel, consulting