DNA Synthesis
100 likes | 288 Vues
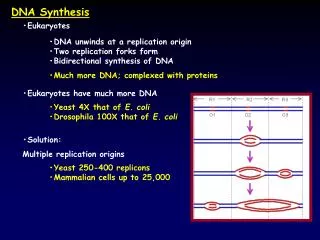
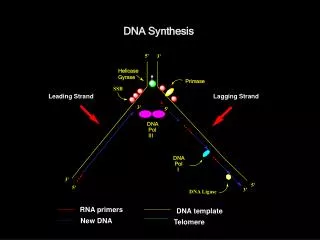
DNA Synthesis. •Eukaryotes. •DNA unwinds at a replication origin •Two replication forks form •Bidirectional synthesis of DNA •Much more DNA; complexed with proteins. •Eukaryotes have much more DNA. •Yeast 4X that of E. coli •Drosophila 100X that of E. coli. •Solution:

DNA Synthesis
E N D
Presentation Transcript
DNA Synthesis •Eukaryotes •DNA unwinds at a replication origin •Two replication forks form •Bidirectional synthesis of DNA •Much more DNA; complexed with proteins •Eukaryotes have much more DNA •Yeast 4X that of E. coli •Drosophila 100X that of E. coli •Solution: Multiple replication origins •Yeast 250-400 replicons •Mammalian cells up to 25,000
DNA Synthesis in Eukaryotes Pre-initiation replication complex: ORC Cdt1 Cdc6 MCM
The Damage and Repair of DNA Two main types of DNA damage: *point mutations *structural changes The molecular basis of point mutations 1. Base substitution (mismatches) transition transversion 2. Tautomeric shift
Gene Mutation The molecular basis of point mutations 3. Base analogs and chemical mutagens
DNA Damage The molecular basis of structural damage 1. Hydrolytic damage Deamination N-glycosidic bond – very weak and easily broken Depurination Deamination
DNA Damage The molecular basis of structural damage 2. Alkylation
DNA Damage The molecular basis of structural damage 3. Oxidation and Radiation