Digital Communications
460 likes | 979 Vues
Digital Communications. Chapter 2 Formatting and Baseband Modulation Signal Processing Lab. Block Diagram of a DCS. Basic Digital Communication Transformations. Formatting and Transmission of Baseband Signal. Seven-bit ASCII. EBCDIC Character Code Set.

Digital Communications
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Digital Communications Chapter 2 Formatting and Baseband Modulation Signal Processing Lab
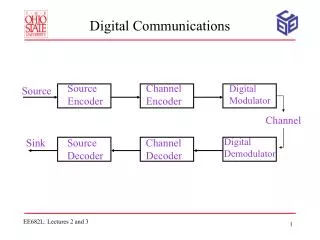
Block Diagram of a DCS Signal Processing Lab., http://signal.korea.ac.kr Dept. of Elec. and Info. Engr., Korea Univ.
Basic Digital Communication Transformations Signal Processing Lab., http://signal.korea.ac.kr Dept. of Elec. and Info. Engr., Korea Univ.
Formatting and Transmissionof Baseband Signal Signal Processing Lab., http://signal.korea.ac.kr Dept. of Elec. and Info. Engr., Korea Univ.
Seven-bit ASCII Signal Processing Lab., http://signal.korea.ac.kr Dept. of Elec. and Info. Engr., Korea Univ.
EBCDIC Character Code Set Signal Processing Lab., http://signal.korea.ac.kr Dept. of Elec. and Info. Engr., Korea Univ.
2.3 Messages, Characters, and Symbols Signal Processing Lab., http://signal.korea.ac.kr Dept. of Elec. and Info. Engr., Korea Univ.
Format Analog Signals • To transform an analog waveform into a form that is compatible with a digital communication, the following steps are taken: • Sampling • Quantization and encoding • Baseband transmission Signal Processing Lab., http://signal.korea.ac.kr Dept. of Elec. and Info. Engr., Korea Univ.
Sampling Signal Processing Lab., http://signal.korea.ac.kr Dept. of Elec. and Info. Engr., Korea Univ.
Sampling(cont´d)Sampling Theorem • Sampling theorem : A bandlimited signal with no spectra components beyond can be uniquely determined by values sampled at uniform intervals of • The sampling rate, is called Nyquist rate Signal Processing Lab., http://signal.korea.ac.kr Dept. of Elec. and Info. Engr., Korea Univ.
Sampling Aliasing(cont´d) Signal Processing Lab., http://signal.korea.ac.kr Dept. of Elec. and Info. Engr., Korea Univ.
Undersampling Signal Processing Lab., http://signal.korea.ac.kr Dept. of Elec. and Info. Engr., Korea Univ.
Quantization and Encoding • Quantization: Sampled values are quantized to values of a finite set. • Pulse code modulation (PCM): Encoding the quantized PAM signals into a digital word (PCM word or codeword). • Each quantized sample is digitally encoded into an ℓ bits codeword where ℓ=log2L and L in the number of quantization level • The analog information can be recovered from the quantized samples, but not precisely • the fidelity increases as the number of quantization level increases. • This causes bandwidth expansion for real-time application Signal Processing Lab., http://signal.korea.ac.kr Dept. of Elec. and Info. Engr., Korea Univ.
Sampling and Quantization Signal Processing Lab., http://signal.korea.ac.kr Dept. of Elec. and Info. Engr., Korea Univ.
Quantization Noise • Quantization noise is a round-off or truncation error which is inversely proportional to the number of quantization levels. • Quantization noise for a uniform (linear) quantizer • Average quantization noise power • Signal peak power • Signal power to average • Quantization noise power Signal Processing Lab., http://signal.korea.ac.kr Dept. of Elec. and Info. Engr., Korea Univ.
PCM Sequence Signal Processing Lab., http://signal.korea.ac.kr Dept. of Elec. and Info. Engr., Korea Univ.
Statistics of Speech Amplitudes • In speech, weak signal are more frequent than strong ones • Adjusting the step size of the quantizer by taking into account the speech statistics improves the SNR for the input range Signal Processing Lab., http://signal.korea.ac.kr Dept. of Elec. and Info. Engr., Korea Univ.
Non-Uniform Quantization Signal Processing Lab., http://signal.korea.ac.kr Dept. of Elec. and Info. Engr., Korea Univ.
Non-Uniform Quantization • Non-uniform quantization implies varying step sizes; smaller steps for weak signals as compared to strong ones • It is done by uniformly quantizing the compressed signal • At the receiver, an inverse compression characteristic, called expansion is employed to avoid signal distortion Signal Processing Lab., http://signal.korea.ac.kr Dept. of Elec. and Info. Engr., Korea Univ.
Companding Characteristics Signal Processing Lab., http://signal.korea.ac.kr Dept. of Elec. and Info. Engr., Korea Univ.
2.8 Baseband Transmission • To transmit information through physical channels, PCM sequences (code words) are transformed to pulses (waveforms). • Each waveform carries a symbol from a set of size M. • Each transmit symbol represents k=log2M bits of the PCM words. • PCM waveforms (line codes) are used for binary symbols (M=2). • M-ary pulse modulation are used for non-binary symbols (M>2). Signal Processing Lab., http://signal.korea.ac.kr Dept. of Elec. and Info. Engr., Korea Univ.
Waveform Representation Signal Processing Lab., http://signal.korea.ac.kr Dept. of Elec. and Info. Engr., Korea Univ.
PCM Waveforms • PCM waveforms category 1. Nonreturn-to-zero (NRZ) 2. Phase encoded 3. Return-to-zero (RZ) 4. Multilevel binary Signal Processing Lab., http://signal.korea.ac.kr Dept. of Elec. and Info. Engr., Korea Univ.
Baseband Transmission (cont´d)PCM Waveforms (cont´d) • Criteria for comparing and selecting PCM waveforms • Spectral characteristics (power spectral density and bandwidth efficiency) • Bit synchronization capability • Error detection capability • Interference and noise immunity • Implementation cost and complexity Signal Processing Lab., http://signal.korea.ac.kr Dept. of Elec. and Info. Engr., Korea Univ.
Spectral Densities of various PCM Waveforms Signal Processing Lab., http://signal.korea.ac.kr Dept. of Elec. and Info. Engr., Korea Univ.
M-ary Pulse Modulation • M-ary pulse modulations category • M-ary pulse-amplitude modulation (PAM) • M-ary pulse-position modulation (PPM) • M-ary pulse-duration modulation (PDM) • M-ary PAM is a multi-level signaling where each symbol takes one of the M allowable amplitude levels, each representing k=log2M bits of PCM words Signal Processing Lab., http://signal.korea.ac.kr Dept. of Elec. and Info. Engr., Korea Univ.
M-ary Pulse-Modulation Waveforms Signal Processing Lab., http://signal.korea.ac.kr Dept. of Elec. and Info. Engr., Korea Univ.
M-ary Pulse Modulation(cont´d) • For a given data rate, M-ary PAM(M>2) requires less bandwidth than binary PCM • For a given average pulse power, binary PCM is easier to detect than M-ary PAM(M>2) Signal Processing Lab., http://signal.korea.ac.kr Dept. of Elec. and Info. Engr., Korea Univ.