The Endocrine System
190 likes | 275 Vues
Explore the functions and importance of the endocrine system, including the role of hormones and the master gland, through a comprehensive study and interactive activities. Learn about puberty, pituitary gland, adrenal glands, and maintaining endocrine health.

The Endocrine System
E N D
Presentation Transcript
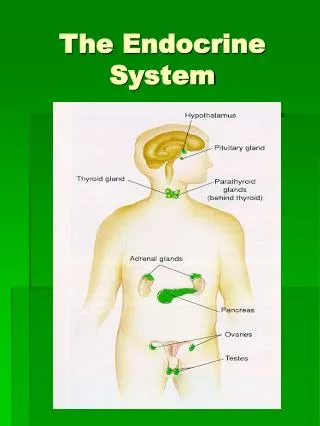
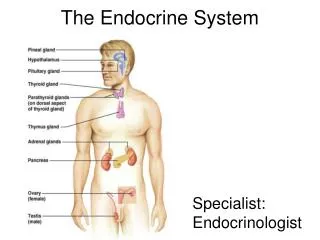
The Endocrine System The Master Gland
BIG Ideas • The endocrine system sends and receive hormones to regulate or control many body functions. • The endocrine system includes various organs that regulate body function.
Objectives • Students will be able to explain the function of the endocrine system after studying its purpose. • Students will understand the purpose of the endocrine system after a pre-test, viewing a video, and a post-test and reading chapter 16, lesson 1 and completing the review questions at the end of the lesson.
Endocrine Pre-test • http://kidshealth.org/kid/htbw/htbw_main_page.html
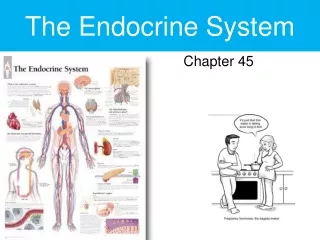
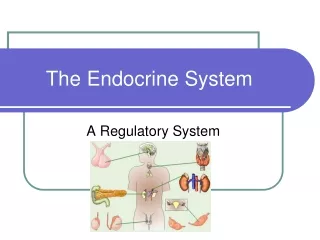
How the endocrine System works • Main Idea—The endocrine system includes various organs that work together to regulate body functions. • Endocrine glands • Hormones
Compare/Contrast • Ductless or tubeless organs or groups of cells • Secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream • Chemical substances • Help to regulate many body’s functions • Carried to their destinations through the bloodstream • Chemical messengers influence physical and mental responses Endocrine Hormones
Hormones and Puberty • During puberty: hormones trigger physical and emotional changes in the body. • Growth is controlled by certain hormones • Too much or too little of certain hormones may contribute to growth disorders. • Factors that may effect hormone levels • Stress • Infection • Changes in the balance of fluids and minerals in the blood
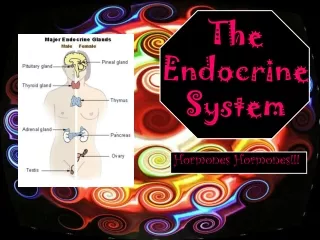
The Pituitary Gland • The Master Gland • Three sections • Anterior lobe • Intermediate Lobe • Posterior Lobe
Anterior lobe or Front lobe I. Anterior lobe or front lobe of the pituitary gland produces these hormones: Somatotropic or growth hormones and development by altering chemical activity in body cells. Thyroid-stimulating hormones (TSH)—stimulates the thyroid to produce hormones Adrenocorticotropic hormones—stimulates production of hormones in the adrenal glands. Follicle-stimulating hormones--(FSH) and luteinizing hormones (LH) to stimulate production of all other sex hormones. These two hormones are secreted by the anterior lobe during adolescence. They control the growth, development, and functions of the gonads, another name for the ovaries and testes. In females: FSH stimulates cells in ovary to produce estrogen, a female sex hormone that triggers the development of ova, or egg cells. LH: is responsible for ovulation and stimulates ovarian cells to produce progesterone—another female hormone The hormone prolactin—stimulates milk production in females who have given birth. In Males: LH stimulates cells in the testes to produce the males hormone testosterone. FSH—controls the production of sperm.
Intermediate Lobe • Middle lobe of pituitary • Secretes melanocyte-stimulating hormone (MSH) • Controls the darkening of the pigments in the skin
Posterior Lobe • Rear lobe of pituitary gland • Secretes antidiuretic hormone (ADH) which regulates the balance of water in the body. • ADH also produces oxytocin, which stimulates the smooth muscles in the uterus during pregnancy, causing contractions during the birth of a baby.
The Adrenal Glands • Purpose of the Adrenal Glands Help body deal with stress and response to emergencies • Two parts • The adrenal cortex • The adrenal medulla
The Adrenal Cortex • Secretes hormone the inhibits the amount of sodium excreted in urine • Maintains blood volume • Maintain blood pressure • Secretes hormones that aid in • Metabolism of fats, proteins, and carbohydrates • Influence • Body’s response to stress • Plays a role in both the • Immune system • Sexual function
The Adrenal Medulla • Controlled by the hypothalamus • Controlled by the autonomic nervous system • Secretes the hormones • Epinephrine and Nor epinephrine • aka –ADRENALINE • Increases hearth beat and respiration , raises blood pressure and suppresses the digestive process during periods of high emotion.
Maintaining Your Endocrine Health • Main Idea—To keep your endocrine system working at its peak, you need to follow sound health practices. • Related to overall health • Eat balanced meals • Use stress management techniques • Teens need 8.5-9 hours of sleep every night • Engage in regular physical activity to keep body strong • Get regular medical check ups
Disorders of Endocrine System • Hormonal • May or may not have recognizable symptoms • Health care professional can perform tests • Disorders • Life long effects • Stress • Infections • Changes in • Balance of fluids and minerals in blood can cause hormone levels to fluctuate. Most can correct themselves. • Serious problems • Diabetes • Hypothyroidism • Hyperthyroidism • Goiter or over production of adrenal hormones may require medication.
Websites • http://health.howstuffworks.com/adam-200091.htm • http://kidshealth.org/PageManager.jsp?lic=1&article_set=59297&cat_id=20607
Endocrine Post Test • http://kidshealth.org/kid/htbw/htbw_main_page.html