Asthma
220 likes | 588 Vues
Learn about the common symptoms, causes, and triggers of asthma. Discover the disparities in asthma prevalence among different demographics and explore the diagnosis process. Find out about effective treatments and how to recognize and avoid triggers.

Asthma
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Meredith G. Hennon, MPH and the Supercourse team in Pittsburgh Asthma
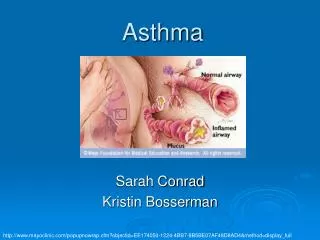
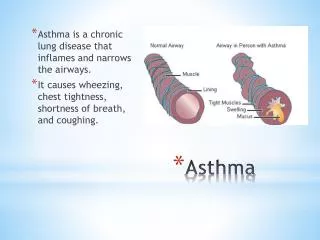
Background • Asthma is a chronic lung-disease that inflames and narrows the airways (tubes that bring air into and out of an individual’s lungs). • Asthma is the most common chronic disease among children.
Symptoms • Common symptoms of asthma include: • Coughing • Wheezing • Tightness in the chest • Shortness of breath
Causes • While the exact cause of asthma is not known, it is thought that a variety of factors interacting with one another, early in life, result in the development of asthma.
Causes • Parents with asthma • Atopy • Childhood respiratory infections • Exposure to allergens or infections while the immune system is developing
Diagnosis • Based on: • Medical history • Physical examination • Test results
Asthma Triggers • A variety of things can cause asthma symptoms to appear: • Allergens • Irritants • Food and drinks • Medicines • Physical activity • Upper respiratory infections (viral)
Asthma prevalence • In the United States: • More females than males have asthma. • Blacks and American Indian/Alaska natives have higher percentages of asthma than Whites, Hispanics, and Asians.
Asthma disparities • Death from asthma is 3 times more likely to occur among Blacks than Whites. • Among adults, women of all races have higher rates of illness and death from asthma than men. • Rates of hospitalization for asthma for Blacks are almost triple those for Whites.
Increasing rates • Asthma rates have been increasing in the United States for both adults and children, males and females, and in the different races and ethnicities. • It is estimated that the number of people with asthma worldwide will increase by 25% in the next 15 years.
Child and Adult Asthma PrevalenceUnited States, 1980-2007 • Child • Adult Lifetime Current 12-Month Source: National Health Interview Survey; CDC National Center for Health Statistics
Asthma Prevalence by SexUnited States, 1980-2007 • Female • Male Lifetime 12-Month Current Source: National Health Interview Survey; CDC National Center for Health Statistics
Asthma Prevalence by Race/EthnicityUnited States, 1997-2007 • Black NH • White NH • Hispanic Lifetime Current Source: National Health Interview Survey; National Center for Health Statistics
Worldwide Burden of Asthma • 300 million people suffer from asthma worldwide. • 255,000 asthma deaths in 2005. • ~3,500 in the United States. • Over 80% of asthma deaths occur in low and lower-middle income countries.
Treatment • While asthma cannot be cured, it can be controlled: • Medications • Long term • Quick relief • Bronchial thermoplasty • Learning to recognize one’s own triggers and taking steps to avoid them.
Treatment • Medication • Long term • Inhaled corticosteroid • Leukotriene modifiers • Long-acting beta agonists • Combination inhalers
Treatment • Quick relief (rescue) medications • Short-acting beta agonists • Ipratropium • Oral and intravenous corticosteroids • Bronchial thermoplasty • Recognizing, tracking, and avoiding triggers
Review Questions (Developed by the Supercourse team) • What are some of the common asthma triggers? • Which age, sex, and/or racial groups see disparities in asthma prevalence rates, as well as hospitalizations and deaths? • Describe the process of asthma diagnosis.