ELASTIC REBOUND THEORY
E N D
Presentation Transcript
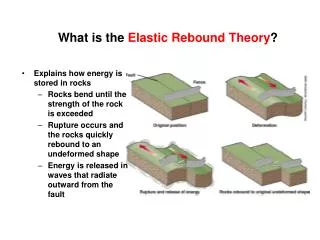
ELASTIC REBOUND THEORY crossing fault trace C.When tectonic forces overcome frictional strength of the fault the crustal blocks suddenly unlock andtremendous pulses of previously stored elastic energy are released. These pulses of energy are the seismic waves we feel in an earthquake. A.Even after large earthquakes occur on a fault, tectonic forces continue to drive the strong but brittle crustal blocks against one another along the fault. Offset streams (locked) B. Elastic strain builds in the crust as the frictional strength of the fault resists the increasing tectonic forces. The crustal blocks remain locked against each along the fault. D. The crust near the fault is temporarily relaxed, but tectonic forces continue to do work. One earthquake cycle has ended as another one begins (see part A).