ECGs
350 likes | 598 Vues
ECGs. Overview. Understand why you get an ECG Identify some common ECG abnormalities. Blood pathway in the heart. Electrical pathway in the heart. Cardiac conduction system. 1. Sinoatrial (SA) node 2. Atrioventricular (AV) node 3. Atrioventricular bundle 4. Left and Right Bundles of His

ECGs
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Overview • Understand why you get an ECG • Identify some common ECG abnormalities
Cardiac conduction system • 1. Sinoatrial (SA) node • 2. Atrioventricular (AV) node • 3. Atrioventricular bundle • 4. Left and Right Bundles of His • 5. Purkinje Fibres • 6. Branch of left bundle branch
Lead placement • V1 - 4th Intercostal space, right sternal border • V2 - 4th Intercostal space, left steral border • V3 - Mid way between V2 and V4 • V4 - 5th Intercostal space, mid clavicular line • V5 - Anterior axillary line, horizontal to V4 • V6 - Mid axillary line, horizontal to V4 and V5
ECG abnormalities • Atrial • Rate • arrthymia • Atioventriclular • Blocks • Ventricular • conduction • Ectopics Unifocal, multifocal • Arrthmias VT, VF • ST segments • Elevation • Depression • Concave
Atria • Sinus bradycardia • Sinus Tachycardia • Atrial Flutter • Atrial fibrillation • SVT
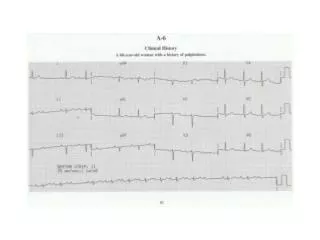
SVT Supraventricular Tachycardia Anything quick originating in the atria Sinus tachycardia Wolf Parkinson White Atrial flutter Atrial fibrillation
A-V Node • 1st degree Prolonged PR interval • 2nd degree intermittent conduction failure • Type I (Wenckebach) conduction velocity progressively slows down until failure of conduction occurs • Type II (Mobitz). is all or none. • N to 1 block • 3rd degree complete conduction failure In addition, 2nd degree heart block occurs in two varieties:
3rd Degree B post pacemaker
Venticular • Conduction • LBBB • RBBB • WILLIAM MARROW • Ectopics • Single • Multiple • Arryhmia • VT • Torsades • VF
Ventricular Tachycardia Ventricular tachycardia