Cell Chemistry: The Essence of Life
240 likes | 333 Vues
Explore the fundamental role of chemistry within cells, from the nature and variety of cells to metabolism, energy processes, and cell division. Understand how cells function and the intricate processes they undergo. Delve into cell membranes, organelles, energy generation, and the fascinating world of mitosis and meiosis.

Cell Chemistry: The Essence of Life
E N D
Presentation Transcript
The Living Cell Chapter 21 Great Idea: Life is based on chemistry, and chemistry takes place in cells
Chapter Outline • The Nature and Variety of Cells • How Does a Cell Work? • Metabolism: Energy and Life • Cell Division
The Cell Theory • All living things are composed of cells • The cell is the fundamental unit of life • All cells arise from previous cells
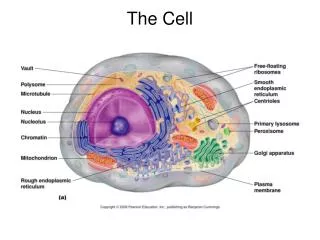
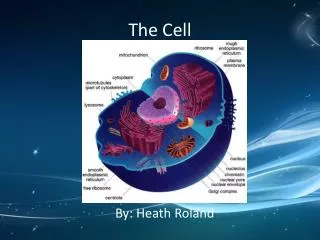
Cell Membranes • Cell Membranes • Isolate cell • Separates cell parts • Transport • Individual molecules • Specific materials • channels • Receptors • Bind molecules • Cell Wall • Plants
The Nucleus • Nucleus • Contains genetic material • Prokaryotes • No nucleus • Eukaryotes • Nucleus • Double Membrane
The Energy Organelles: Chloroplasts and Mitochondria • Organelle • Specialized structure in cell • Chloroplasts • Energy transformation • chlorophyll • Plant cells only • Double membrane • Mitochondria • Produces cells energy • Double membrane • Own DNA
Cytoskeleton • Cytoskeleton • Gives cell shape • Anchors • Allows movement • Transport system • Within cell • Structure • Strong filaments • Complex web
The Cell’s Energy Currency • Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) • Provides energy • Structure • 3 phosphate groups • Sugar molecule: ribose • adenine • Function • Removal of phosphate group provides energy
Photosynthesis • Photosynthesis • Convert sunlight to energy • Process • Energy + CO2 + H2O carbohydrate + O2 • Colors
Glycolysis: The First Step in Energy Generation in the Cell • Respiration • Oxidation of carbohydrate • Retrieves energy in glucose • Aerobic • Process • Glycolysis • Split glucose • Result • Pyruvic acid • 2 ATP • 2 energy carriers • Convert energy carriers to 2-3 ATP • 1 molecule glucose = 6-8 ATP
Fermentation: A Way to Keep Glycolysis Going • Fermentation • Anaerobic • Inefficient • Yeast • alcohol • Animal cells • Lactic acid
The Final Stages of Respiration • Krebs cycle • Glucose broken down • CO2 produced • ATP • Energy-carrying molecules • Result • 36-38 ATP
Mitosis • Mitosis • Cell division • Not for sexual reproduction • Chromosomes • Process • Copy chromosomes • Spindle fibers • Migration of chromosomes • Nuclear membrane reforms
Meiosis • Meiosis • Sexual reproduction • 1 cell forms 4 gametes • Gametes are genetically unique • Process • Copy chromosomes • Crossing over • Segregation • Segregation again • Result • 4 daughter cells • ½ normal chromosomes