RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS
900 likes | 7.15k Vues
RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS. CASE PRESENTATION - 34 YEAR OLD FEMALE. Presented to family physician c/o Mild stiffness in fingers and wrists upon awakening for past month Stiffness lasted for approximately 1 hour

RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS
E N D
Presentation Transcript
CASE PRESENTATION - 34 YEAR OLD FEMALE • Presented to family physician c/o • Mild stiffness in fingers and wrists upon awakening for past month • Stiffness lasted for approximately 1 hour • Nine months later, family physician was seen when swelling appeared in fingers and wrists and fatigue • Laboratory tests • Complete blood count (CBC) • Rheumatoid factor (RF) • C-reactive protein (CRP) • Anti-nuclear antibody (ANA)
CASE PRESENTATION -34 YEAR OLD FEMALE • Laboratory Test Results Reference Ranges • CBC • Mild anemia • Rheumatoid factor (RF) • Positive at a titer of 1:80 (< 1:40) • C-reactive protein (CRP) • 30 mg/L (< 8.0 mg/L) • Anti-nuclear antibody (ANA) • Negative (Negative)
CASE PRESNTATION - 34 YEAR OLD FEMALE • Diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis • Family history • Negative for rheumatoid disease • Treatment • Aspirin 325 mg TID
CASE PRESNTATION - 34 YEAR OLD FEMALE • One year later, referred to Rheumatologist as joints became more stiff and painful • Physical exam revealed spongy swelling in joints (thickening of synovium) • Prescribed non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) • Ibuprofen (Motrin) 600 mg QID • 1 year later, continued thickening of synovium, prescribed • Hydroxychloroquine (Plaquenil)
CASE PRESENTATION -34 YEAR OLD FEMALE • At 42 years of age • RF by LA was positive at titer of 1:2560 • X-rays showed erosion of a number of joints • At 45 years of age, prescribed methotrexate for exacerbation of symptoms • At age 51, symptoms continued to worsen, prescribed infliximab (Remicade)
CASE PRESENTATION -61 YEAR OLD FEMALE • Presents with 3 month history of asymptomatic lesions on lower legs • History • Rheumatoid arthritis treated with • Prednizone and etanercept (Enbrel) • No recent leg trauma • Biweekly pedicures • Biopsy of two lesions submitted for • Histopathology • Routine culture
CASE PRESENTATION -61 YEAR OLD FEMALE • Histopathology • H and E • Necrotizing, granulomatous inflammation • Acid-fast stain • Positive for few acid-fast bacilli (AFB) • Routine culture • No organisms seen on gram stain • Culture positive for • Rapid growing acid-fast bacilli • Mycobacterium mucogenicum identified
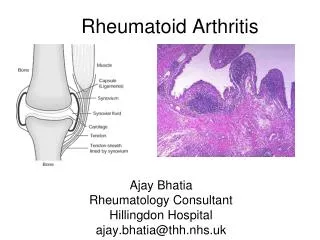
RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS • Chronic systemic inflammatory disease affecting synovial membranes and articular structures of multiple joints • Etiology is unknown • Female:Male ratio is 3:1 • Age of onset usually between 25 and 50 years • Prevalence of 1% in US
RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS • Risk factors • Smoking • Pathophysiology • Infectious triggers, genetic predispostion and autoimmune response • Infectious triggers • Mycoplasma, parvovirus B19, HHV-6 and Epstein-Barr virus • “Mistaken identity” (“molecular mimicry”) theory • Genetic predisposition • HLA-DR4 • 65% of caucasians with RA
RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS • Autoimmune response • Inflammation and hyperplasia of synovium • CD4 TH1 cells activate macrophages and synovial fibroblasts to produce cytokines • TNF-alpha, IL-1, IL-6, IL-15 and IL-17 • Osteoclasts and chondroclasts are activated • CD4 TH2 cells activate B cells
DIAGNOSIS OF RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS – AMERICAN COLLEGE OF RHEUMATOLOGY • Morning stiffness of > 1 hour • Arthritis involving 3 or more joints • Arthritis of hand joints • Symmetric arthritis • Subcutaneous nodules • Positive test for rheumatoid factor (RF) • Radiographic evidence of RA
LABORATORY DIAGNOSIS OF RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS • Complete blood count (CBC) • Rheumatoid factor (Latex agglutination) • Screen and titer • Rheumatoid factor (Nephelometry) • IgM, IgG and IgA • Cyclic citrullinated peptide (CCP) antibody • C-reactive protein (CRP) • Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) • Anti-nuclear antibody (ANA)
RHEUMATOID FACTORS • Autoantibodies (IgM, IgG and IgA) to Fc region of IgG • 80% of patient’s with RA show RF • RF by Latex Agglutination • Latex particles coated with human IgG • Screen with reflex titer • Reference range of < 1:40
RHEUMATOID FACTORS • RF by Nephelometry • Reported in IU/mL • Reference range (< 20 IL/mL) • Rheumatoid Factor IgM • Most consistent finding • Rheumatoid Factor IgG • High specificity for RA and strong correlation with vasculitis • Rheumatoid Factor IgA • Prognostic for more severe disease
CYCLIC CITRULLINATED PEPTIDE (CCP) ANTIBODY • Circular peptide containing citrulline • Citrulline is produced by citrullination (Deimidation) • Citrullination (Deimidation) • Post-translational modification of arginine • Peptidylarginine deiminase (PAD) • Proteins containing citrulline • Myelin basic protein, filaggren, fibrinogen, vimentin, EBV nuclear antigen 1
CYCLIC CITRULLINATED PEPTIDE (CCP) ANTIBODY • Autoantibodies in RA react with a number of citrullinated proteins / peptides • Fibrinogen, EBV nuclear antigen 1, vimentin • Vimentin • Secreted and citrullinated by macrophages • Response to apoptosis • Response to pro-inflammatory cytokine TNF-alpha • EIA for IgG to anti-citrullinated proteins/peptides • Sensitivity (80%) and specificity (97%) • Reference range < 5.0 U/L • Detected earlier than RF • Indicator of more severe disease and disease in future
ERYTHROCYTE SEDIMENTATION RATE (ESR) • Sedimentation rate (Sed rate) • Non-specific measure of inflammation • Specific analyte not measured • Physical phenomenon with many variables • Fibrinogen causes RBC’s to stick together • Distance (mm) erythrocyte layer moves in 1 hour • Reference range (Westergren method) • < 15 mm/hr (Males < 50) • < 20 mm/hr (Females < 50)
ERYTHROCYTE SEDIMENTATION RATE (ESR) • Automated and semi-automated methods • More rapid results • Less sensitive than CRP • Elevation within 5 to 7 days • Simple and inexpensive
C-REACTIVE PROTEIN (CRP) • Marker for (acute) inflammation • Infection, cancer, autoimmunity, trauma, hypersensitivity • Origin of name • Reacts with “C polysaccharide” of pneumococcus • Mechanism of action • Binds to phosphocholine on dead/dying cells and pathogens • Activates classical complement pathway
C-REACTIVE PROTEIN (CRP) • Produced by liver in response to IL-6 • More sensitive than ESR • Elevation within 6 hours • Peak within 48 hours • Laboratory method • Nephelometry
C-REACTIVE PROTEIN (CRP) • Reference range • < 8.0 mg/L • Acute inflammation • Greater than 10 mg/L • Viral infection (10 to 40 mg/L) • Bacterial infection (40 to > 200 mg/L) • Cardiac risk stratification • Low risk: < 1.0 mg/L • Average risk: 1.0 to 3.0 mg/L • High risk: > 3.0 mg/L
ANTINUCLEAR ANTIBODY (ANA) TEST • Detects autoantibodies against nuclear antigens • Nuclear antigens • DS-DNA, SS-A, SS-B, histones • Laboratory methods • Enzyme immunoassay (EIA) • Indirect immunofluorescence assay (IFA) • Positive results • Rheumatoid arthritis (25-90%)
TREATMENT OF RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS • Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) • Aspirin • Ibuprofen (Advil and Motrin) • Naproxen (Aleve) • Celecoxib (Celebrex) • Corticosteroids • Prednizone • Analgesic drugs • Acetaminophen
TREATMENT OF RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS • Disease Modifying Anti-Rheumatic Drugs (DMARDs) • Methotrexate (Rheumatrex) • Hydroxychloroquine (Plaquenil) • Azathioprine (Imuran) • Cyclophosphamide (Cytoxan) • Cyclosporine (Sandimmune) • Minocycline (Minocin) • Biological Response Modifiers (Biologic DMARDs) • Tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) inhibitors • Etanercept (Enbrel) • Infliximab (Remicade) • Adalimumab (Humira) • Golimumab (Simponi)
TREATMENT OF RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS • Biological Response Modifiers (Biologic DMARDs) • B cell depleting agents • Rituximab (Rituxan) • T-cell co-stimulatory blocking agents • Abatacept (Orencia) • Interleukin-1 (IL-1) receptor antagonist • Anakinra (Kineret) • Interleukin-6 (IL-6) receptor antagonist • Tocilizumab (Actemra)
ETANERCEPT (ENBREL) • Dimeric fusion protein • Extracellular binding domain of p75 TNF receptor and the Fc portion of human IgG1 • Prevents binding of TNF-alpha to cell surface receptor • Adverse reactions • Infections, Malignancies, Autoimmunity
INFLIXIMAB (REMICADE) • Chimeric IgG1 monoclonal antibody • Human (constant region) • Mouse (variable region) • Prevents binding of TNF-alpha to receptor • Administration is IV along with methotrexate • 10 to 30% anti-infliximab antibodies • Adverse effects • Infections, Malignancies, Autoimmunity
ADALIMUMAB (HUMIRA) • Human IgG1 monoclonal antibody • Binds to TNF-alpha and prevents binding of TNF to p55 and p75 cell surface receptors • Adverse reactions • Infections • Malignancies • Autoimmunity
ABATACEPT (ORENCIA) • Soluble fusion protein • Extracellular domain of human cytotoxic T-lymphocyte associated antigen 4 (CTLA-4) • Fc region of human IgG1 • Indication in RA • Adults with moderate to severe RA with inadequate response to one or more TNF-alpha antagonist therapies • Administered by 30 minute IV infusion • Concurrent therapy with TNF-alpha inhibitors not recommended
ABATACEPT (ORENCIA) • CTLA-4 • Expressed on surface of CD4 T cells • Binds to CD80 and CD86 and transmits inhibitory signal • Mechanism of action • Binds to CD80 (B7.1) and CD86 (B7.2) on APC • Blocks access to CD28 co-stimulatory receptor on T cells • Activation of T cells by APC • Stimulation by MHC class II molecule to TCR • Co-stimulation by B7 to • CD28 (stimulation) • CTLA4 (inhibition)
ANAKINRA (KINERET) • Recombinant, nonglycosylated protein • Synthetic version of human endogenous IL-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1Ra) • Indication in RA • Adults with moderate to severe RA with inadequate response to one or more DMARD agents • Administered by daily subcutaneous injection • Not compatible with TNF-alpha inhibitors
ANAKINRA (KINERET) • Normal joint • Endogenous IL-1Ra competes with IL-1 for IL-1 receptor type I (IL-1RI) • IL-1Ra most important regulator of synovial IL-1 activity • RA joint • Higher level of IL-1 compared to IL-1Ra • Mechanism of action • Binding of IL-1Ra competitively inhibits binding of IL-1 to IL-1 receptor type 1 (IL-1RI)
RITUXIMAB (RITUXAN) • Chimeric IgG1 monoclonal antibody • Variable domains are mouse • Constant domains are human • FDA approval • 1997 for non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma (NHL) • 2006 for rheumatoid arthritis (RA) • Indication in RA • Adults with moderate to severe RA with inadequate response to one or more TNF-alpha antagonist therapies
RITUXIMAB (RITUXAN) • Mechanism of action • Binds to CD20 antigen on normal and malignant B lymphocytes and mediates lysis • Mechanisms of B cell lysis • Complement • ADCC • Induction of apoptosis • CD20 antigen not present on • Hematopoietic stem cells, proB cells and normal plasma cells