The Evolution of Humanity: Creation, Adaptation, and Survival
270 likes | 396 Vues
This comprehensive overview explores the origins of humans, tracing their evolution from ancient species like Australopithecus to modern Homo sapiens. It contrasts creationism with Darwin's theory of evolution, highlighting evidence from fossil records and paleoanthropology. The study of human social systems reveals the moral principles guiding societies and their interaction with nature. Discover the significance of notable fossils, the impact of the Out of Africa model, and the role of culture in early human life, including cave art and tool-making practices.

The Evolution of Humanity: Creation, Adaptation, and Survival
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Purpose of Creation Story • Define moral principles of a society • Guide dealings with nature and supernatural • Explain human social systems and daily life
Creationism/Evidence • Belief in the creation bible story taken as is, not symbolically • Archbishop James Ussher followed the lifespans of people in the bible backwards from the date of Jesus’ birth and suggested that 4004 BC was the earth’s creation date.
Charles Darwin and Evolution • On the Origin of Species (1859) and The Descent of Man (1871) • Biological life around a lot longer than we thought • Natural selection- biological variations enhance species’ survival- humans a part of natural selection • species that cannot adapt to changing environment and conditions eventually become extinct • major source of evidence for evolution is the fossil record that shows change in animal development over time
Paleoanthropology • the study of ancient humans • concerned with where we came from; how fossils are related
Piltdown Man • hoax of a discovered fossil believed to be the first “Englishman” in 1912 • 1953, proved it a fake and the importance of scientists checking each other’s work continued!
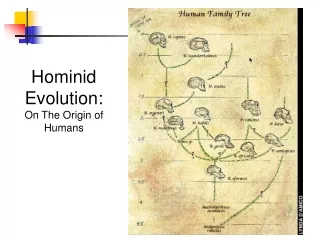
Human Evolution • Hominids in the primate family- first appeared 7 million years ago • Humans most closely related to chimps and gorillas • Major traits distinguish humans from other primates • -manner of movement (locomotion) • - an upright position, which is known as “Bipedal” • -A large organized brain is another feature, along with a diminished face and teeth. • -Use and construction of tools are notable characteristics of Hominids
Who is related to who?? • See links on website
Lucy- David Johanson (1974) • Our most ancient ancestor is Australopithecus afarensis. They lived roughly 4 - 2.75 million years ago. " Lucy" is the skeleton remains of an Australopithecus afarensis which has made us aware of this species. Males and females show a considerable difference in size, varying from 1 - 1.7 m in height and from 25 - 50 kg in weight. This bipedal ancestor had a brain capacity that fluctuated from 380 - 450 cc. • Johansonalso discovered the “First Family” a group of fossils, that allowed Johanson to make conclusions about Lucy.
Australopithecus africanus • Australopithecus africanus inhabited the earth roughly 3 - 1.6 million years ago. The characteristic difference between the Ausrtalopithicusafarenis and africanus is the height and brain capacity. The height of the africanus is 1.4 m and the brain capacity is approximately 400 - 600 cc. Smaller incisor teeth and a slightly flatter face are also noted. The afarensis has a height of 1.2 m and a cranial capacity of 380 - 450 cc. Sticks, and stones were most likely used to gather food by the Australopithecus africanus.
Homo Erectus • •The first species to migrate from Africa during the Pleistocene glacial period was Homo erectus. This species was widely disbursed in the time frame of 1.8 - 1 million years ago.
Homo Sapiens • •The evolution of Homo sapiens commenced approximately 200 000 - 300 000 years ago. The Homo sapiens structure is similar to that of the Homo erectus, yet Homo sapiens skulls were slightly rounder and larger. Brain was a third larger than Homo erectus.
Neanderthal Man • A dead end on the evolutionary tree is the Neanderthal. The skull of a Neanderthal was not only low and long but had a heavy, notable brow. Its mouth projected above its chin, which receded.
Out of Africa • Homo sapiens spread out from Africa • weather, abundance of food, population increase (Homo sapiens sapiens- modern human) • minor evolutionary changes occurred i.e. skin colour • changed their habits to adapt
Out of Africa • See links on website
The Stone Age • The Stone Age (2 Million years ago – 4,000 years ago) • Encompasses many cultures and subperiods. • The Paleolithic (Old Stone Age) lasted until about 10,000 years ago, 3000 years after the last ice age. • The Neolithic (New Stone Age) is associated with the origins of agriculture, followed.
Cro-Magnon • In Europe, Homo Sapiens Sapiens are called Cro-Magnon, named after the French cave in which the original find was made in 1868. • Neanderthals of Europe would slowly disappear and Cro-Magnon survived.
Humans were foragers- hunting and food gathering people • lots of vegetables, meat was common at feasts • Stone tool making was the first recognizable cultural activity • made from stone, bone, skins, and wood • skillful hunter, intelligence plus tools • set fires deliberately • lived in small groups- big enough to share responsibilities, small enough not to exhaust food supply
Cave art found at Lascaux Caves in France • show deer, horses, bison, and animals that are now extinct • Figurines found that are now called Venus Figurines • Suggested that they may represent fertility symbols that were connected with the worship of a mother goddess • Some cave art and artifacts from graves suggest that Stone Age people had well-developed religions, but without written texts it is hard to know what they believed.
Agriculture Revolution • See links on website
Homework • Read p.6-14 in your textbook. • Identify and state the significance of the following terms: • Stone Age, Paleolithic, Neolithic, foragers, agricultural revolutions, CatalHuyuk • Answer: How did agriculture change the lifestyle of those who practiced it?