Plot Diagram
120 likes | 386 Vues
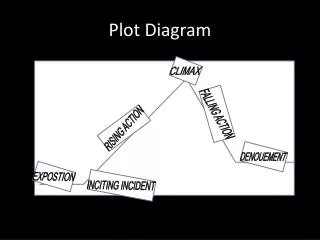
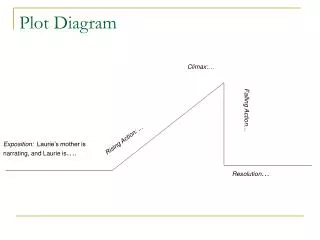
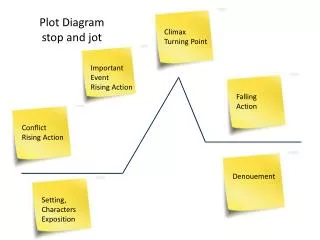
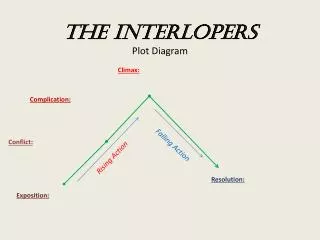
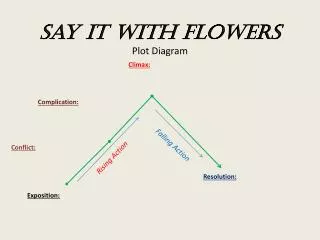
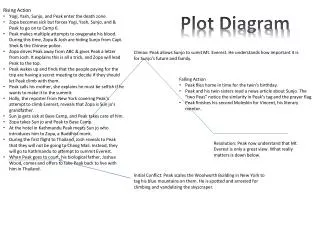
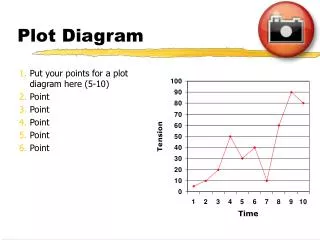
CLIMAX. FALLING ACTION. RISING ACTION. DENOUEMENT. EXPOSTION. INCITING INCIDENT. Plot Diagram. C onflict. -a struggle between two opposing forces -Man v. Man -Man v. Self -Man v. Nature -Man v. Society. Exposition. -occurs at the beginning of a story

Plot Diagram
E N D
Presentation Transcript
CLIMAX FALLING ACTION RISING ACTION DENOUEMENT EXPOSTION INCITING INCIDENT Plot Diagram
Conflict • -a struggle between two opposing forces • -Man v. Man • -Man v. Self • -Man v. Nature • -Man v. Society
Exposition • -occurs at the beginning of a story • -characters (protagonist and antagonist), conflict, and setting are introduced
Inciting Incident • -Interrupts the pace and balance of the situation and is the one event in the story’s action without which there would be no story
Rising Action • This part of the story begins to develop the conflict(s). A building of interest or suspense occurs. • -obstacles that interfere with the protagonist’s efforts to reach the goal
Climax • -turning point of the story • -Usually the main character comes face to face with a conflict • -The main character will change in some way.
Falling Action • -All loose ends of the plot are tied up. • -The conflict(s) and climax are taken care of.
Denouement (Resolution) • -The final outcome of the main dramatic complication in a literary work. • -The protagonist is either: better off than at the beginning of the story or worse off than at the beginning of the story
Elements of Literature • Theme • Statement, lesson, moral • What the text is saying about life • Mood • Atmosphere in the story • MOOD=ME • Tone • Attitude of the AUTHOR toward the reader or subject matter of a literary work • Can be playful, humorous, serious, mocking, angry, commanding, apologetic, or colloquial • Shown through the language of the story
Language of the Story • Colloquial • Of or relating to conversation – everyday language • Also, unacceptable or informal • Dialect • A regional variety of language • Characterized by features of grammar, regional varieties, pronunciation, or slang • Slang • Informal non-standard vocabulary • Characterized by coinages, arbitrarily changed words and figures of speech
Point of View • First Person • Narrator is the main character • Tells the story using “I” • Third Person Limited – narrator focuses on only one character’s thoughts and feelings • Omniscient • Narrator knows everything about the characters and problems in the story as if from above (all-knowing) • He does not take part in the story
Allusions • Mercury • Mythological allusion • A Roman god of commerce, eloquence, travel, cunning, and theft who serves as a messenger to the other gods • Chopin’s Waltzes – Frederic Chopin, a Polish pianist and composer in the 1800’s • http://safeshare.tv/w/MKSyHxYXdf • Dodge City – onetime rowdy cowboy town under the supervision of Bat Masterson and Wyatt Earp • Miss Quicksilver • Liquid mercury • Reference to the speed with which it flows