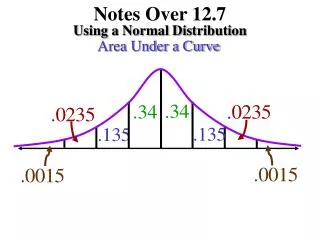
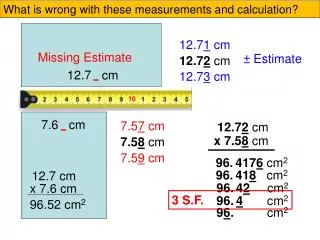
Chapter 12.7
80 likes | 248 Vues
Chapter 12.7. Examples of X-Linked Inheritance Patterns . AP Biology Fall 2010. X-Linked Inheritance Characteristics . The mutated recessive gene occurs only on the X chromosome Heterozygous females are phenotypically normal

Chapter 12.7
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Chapter 12.7 Examples of X-Linked Inheritance Patterns AP Biology Fall 2010
X-Linked Inheritance Characteristics • The mutated recessive gene occurs only on the X chromosome • Heterozygous females are phenotypically normal • Males are more often affected because the single recessive allele (on the X chromosome) is not masked by a dominant gene on any other chromosome
X-Linked Inheritance Characteristics • A normal male mated with a female heterozygote has a 50% chance of producing carrier daughters and a 50% chance of producing affected sons • In the case of a homozygous recessive female and a normal male, all daughters will be carriers and all sons affected • Can you perform these crosses?
Hemophilia A • A serious X-linked recessive condition is hemophilia A (affecting 1 in 7,000 males) • Is the inability of the blood to clot because the genes do not code for the necessary clotting agent(s) • The disorder frequency was high among the royal families of Europe and Russia in the nineteenth century • Why?
Red-Green Colour Blindness • Colour blindness: is the inability to distinguish some or all of the colours in the visible light spectrum • Mutated genes change the light-absorbing capacity of sensory receptors of the eyes • Red-green colour blind people can see fewer than 25 of the 150 differences in colour seen normally • It is 12 times more common in men than women
Red-Green Colour Blindness • Ishihara plates: • Do you see a 7 or 29? • Do you see a 3 or 8? • 29 and 8 are normal , 7 and 3 are colour blind
Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy • Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD): is characterized by rapid degeeration of muscles early in life • One in 3,500 males • Is caused by a recessive allele for a structural protein called dystrophin • When dystrophin is absent or abnormal, muscle cells progressively die (in an unstoppable manner) • Diagnosed between the ages 3 to 7, the affected boy generally dies before he reaches 25
X-Linked Inheritance • More than 300 connections to known genetic disorders have been identified on the X chromosome • Does this mean women are superior? ; )