Ocean pH
40 likes | 217 Vues
Ocean pH. Acids and Bases H2O can dissociate (break apart) to form H+ and OH- Neutral solution- concentration of H+ and OH- are equal Acidic solution – more H+ than OH- Basic (alkaline) solution – more OH- than H+ ions. pH scale- measures acidity or alkalinity of solutions

Ocean pH
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Ocean pH • Acids and Bases • H2O can dissociate (break apart) to form H+ and OH- • Neutral solution- concentration of H+ and OH- are equal • Acidic solution – more H+ than OH- • Basic (alkaline) solution – more OH- than H+ ions
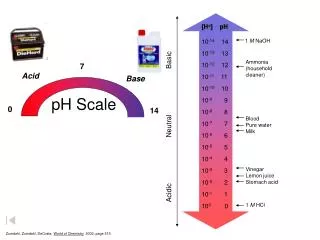
pH scale- measures acidity or alkalinity of solutions • pH= 7: neutral (pure water0 • pH> 7: basic; alkaline (low concentrations of H+) • pH < 7 : acidic (high concentrations of H+)
pH of seawater: slightly alkaline ( pH = 7.5- 8.5) • Relatively constant due to buffering action of CO2 • Buffer- substance that prevents sudden or large changes in pH of a solution • Seawater’s buffer: C Carbon dioxide carbonic acid bicarbonate • Water to alkaline: reaction goes to right, releasing H+ • Water too acidic: reaction goes to left, removing H+ • Important to organisms requiring stable pH