Understanding Addictive Behaviors: Prevention Models and Interventions Quiz
110 likes | 216 Vues
Dive into the complexities of addictive behaviors with this comprehensive quiz covering models of prevention and various interventions. Explore the Theory of Reasoned Action (TRA) and Theory of Planned Behavior (TPB), their criticisms, and the research that supports their effectiveness. Discover biological interventions such as methadone and naltrexone, psychological strategies like CBT, and public health initiatives aimed at reducing addiction-related harm. Test your knowledge with insightful questions that address key concepts and findings in addiction research.

Understanding Addictive Behaviors: Prevention Models and Interventions Quiz
E N D
Presentation Transcript
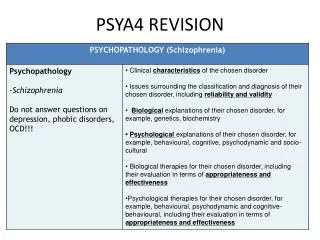
PSYA4 Addictive Behaviour Pub Quiz 2 Models of Prevention and Types of Interventions
Round 1 • What does TRA stand for? 1 • Who first described the TRA? 1 • Which factors is intention a function of? 2 • What is alcohol myopia? How might it affect a person’s ability to give up an addiction? 2 • How is the TRA culture biased? 1
Round 2 • What does TPB stand for? 1 • How is the TPB different to the TRA? 1 • What research evidence is there that the TPB is better than the TRA? 1 • Why are the TRA and TPB criticised for being too rational? 1 • What type of research did Armitage and Conner do and what did they find? 2
Round 3 • Name 2 Biological interventions. 2 • How does methadone work? 1 • How does naltrexone reduce the urge to gamble? 1 • Give one limitation of Hollander’s research using SSRIs. 1 • Give one problem with methadone treatment. 1
Round 4 • Name 2 psychological interventions. 2 • What did Sindelar find when he rewarded those on methadone treatment with money rewards?1 • Give one limitation of giving rewards. 1 • How does CBT help addicts? 1 • What does intervention bias mean in terms of addiction? 1
Round 5 • Name 2 Public Health Interventions. 2 • What was the primary objective of the smoking ban in 2007? 1 • Name the 4 conditions in the NIDA study. Which condition proved most effective? 5 • What did West find in 2009 to suggests the smoking ban was less effective than expected? 1 • What did Beckham et al find in 2008? 1
Answers - Round 1 • What does TRA stand for? 1 • Theory of reasoned action • Who first described the TRA? 1 • Ajzen and Fishbein, 1975 • Which factors is intention a function of? 2 • Personal (behavioural attitude) and Social (subjective norms) • What is alcohol myopia? How might it affect a person’s ability to give up an addiction? 2 • Alcohol decreasing cognitive capacity • Might be under influence of alcohol or drugs so does not carry out intended behaviour i.e giving up • How is the TRA culture biased? 1 • Developed in USA an individualistic culture. Different results in Japan and China
Answers Round 2 • What does TPB stand for? 1 • Theory of Planned Behaviour • How is the TPB different to the TRA? 1 • Also includes Perceived behavioural control – how well the individual thinks they will be able to perform the behaviour • What research evidence is there that the TPB is better than the TRA? 1 • Armitage and Conner 2001 – 6% more intention • Why are the TRA and TPB criticised for being too rational? 1 • Don’t take emotions, compulsions or other irrational determinants of behaviour into account • What type of research did Armitage and Conner do and what did they find? 2 • Meta analysis. Successful in predicting intyention to change rather than actual behavioural change,
Answers - Round 3 • Name 2 Biological interventions. 2 • Methadone, naltrexone, SSRIs • How does methadone work? 1 • Mimics effects of heroine but less addictive • How does naltrexone reduce the urge to gamble? 1 • Reduces rewarding and reinforcing properties of gambling behaviour • Give one limitation of Hollander’s research using SSRIs. 1 • Small sample size, short duration • Give one problem with methadone treatment. 1 • Can become addicted to it, black market, 300 deaths in UK in 2007
Answers - Round 4 • Name 2 psychological interventions. 2 • Reinforcement, CBT • What did Sindelar find when he rewarded those on methadone treatment with money rewards?1 • Drug use dropped dramatically • Give one limitation of giving rewards. 1 • Do not address problem that caused the addiction • How does CBT help addicts? 1 • Help people change the way they think about their addictive behaviours • What does intervention bias mean in terms of addiction?1 • Only see addict when condition well advanced so think it is difficult to treat. Screening would alleviate this.
Answers - Round 5 • Name 2 Public Health Interventions. 2 • NIDA, Quitline, Smokefree, Drink Aware, Gambling Aware, FRANK • What was the primary objective of the smoking ban in 2007? 1 • Protect workers from second-hand smoke • Name the 4 conditions in the NIDA study. Which condition proved most effective? 5 • 1. Group drug counselling (GDC)alone, 2. GDC and CBT, 3. GDC and supportive/expressive psychotherapy, 4. Individual drug counselling and GDC. Condition 4 • What did West find in 2009 to suggest the smoking ban was less effective than expected? 1 • Rebound effect after the ban – more gave up before the ban. • What did Beckham et al find in 2008? 1 • More likely to quit with a combination of counselling and medication