Glacial Features
200 likes | 707 Vues
Glacial Features. How Glaciers Re-Shape the Land. Weathering vs. Erosion What’s the difference?. Weathering = Breakdown of rock Erosion = Transport of sediments. …the rock surface below it gets scraped and weathered. As a glacier moves …. Rock.

Glacial Features
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Glacial Features How Glaciers Re-Shape the Land
Weathering vs. ErosionWhat’s the difference? • Weathering = Breakdown of rock • Erosion = Transport of sediments
…the rock surface below it gets scraped and weathered. As a glacier moves … Rock
Scratch marks in the rock are called ‘STRIATIONS’ What could you tell if you found these? • A glacier was present in the past. • The direction that the glacier moved.
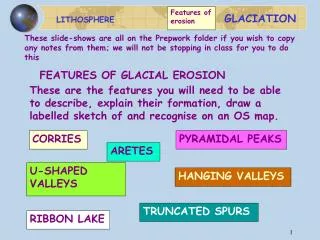
Other Common Glacial Features Horn Arete Cirque Hanging Valley Main U-Shaped Valley
The weathering of rock by glacial ice can cause… …a circular shaped bowl at the base of mountain peaks, called a CIRQUE. This is found at the ‘start’ of many alpine glaciers.
What is this and how was it formed? Arete Two glaciers moving next to each other leave a narrow ridge between them.
What is this and how was it formed? Horn When several cirques form in different directions from a single mountain peak.
Which feature was formed by a glacier? How can you tell?
Sediment deposits left by glaciers There are two main types: • Glacial Till —Unsorted (containing both large and small particle sizes) • Glacial Outwash —Sorted (particles of a given layer all have the same size) This happens due to the fact that sometimes the sediments are dropped by running water and other times they are dropped by melting ice.
Glacial Till can be found in several different forms: A Moraine is a ‘Hill of Till’. • Terminal Moraine— the hill of till found at the farthest advance of the glacial ice front. • Recessional moraine— a hill of till found behind the terminal moraine which formed while the glacier retreated. • Lateral Moraine— a hill of till found to the side of the glacier.
How do moraines form? • Click here
Glacial Erratic • Large boulders that are not similar to the bedrock of the area. • They were carried to this place by moving glacial ice which later melted.
Glacial Outwash • What are its characteristics? • How does it get there?
These depressions are called kettlesorkettle lakes. • How would a glacier cause these to form?