Understanding Loops in C Programming: For, While, and Do-While
200 likes | 354 Vues
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of loop constructs in C programming, focusing on `for`, `while`, and `do-while` loops. Each loop type is explained with examples to demonstrate their structure and usage. Learn how to iterate over ranges with the `for` loop, control execution based on conditions with the `while` loop, and ensure at least one execution with the `do-while` loop. Discover practical applications such as printing patterns and tables, essential for deepening your programming skills.

Understanding Loops in C Programming: For, While, and Do-While
E N D
Presentation Transcript
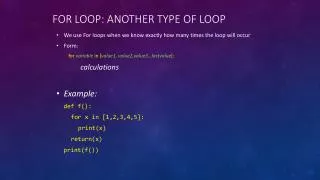
for(…) {…} • for (expression;condition;increment) • statement; • ----------- หรือ ------------------------------- • for (expression;condition;increment) • {statement; • statement; • statement; • }
for(…) {…} • int i • for ( i=1;i<10;i=i+1) • printf( “*” ) ; • ----------- หรือ ------------------------------- • int i • for (i=1;i<10;i=i+1) • {printf( “*****” ) ; • printf( “*****\n” ) ; • }
1 2 3 4 for(…) {…} • for ( int i=1;i<10;i=i+1) • printf( “*” ) ; • ----------- หรือ ------------------------------- • for (int i=1;i<10;i=i+1) • {printf( “*****” ) ; • printf( “*****\n” ) ; • } 1 2 4 N 3 Y
for(…) {…} • for (int i=1;i<=25;i=i+1) • { • printf( “*” ) ; • if((i%5)= =0 ) printf( “\n” ) ; • }
for(…) {…} • scanf(“%d”,&n); • for (int i=1;i<=(n*n);i=i+1) • { • printf( “*” ) ; • if((i%n)= =0 ) printf( “\n” ) ; • }
while(…) while (condition) statement ; -- หรือ -- while (condition) { statement ; statement ; statement ; }
N 1 2 3 4 Y while(…) {…} • int i= 1; • while (i<=25) • { • printf( “*” ) ; • if((i%5)= =0 ) printf( “\n” ) ; • i=i+1; • } 1 2 3 4
do { ... } while(…); do statement ; while ( condition ) ; -- หรือ -- do { statement ; statement ; … } while ( condition ) ;
N Y 1 2 4 3 do {…} while(…); • int i= 1; • do{ • printf( “*” ) ; • if((i%5)= =0 ) printf( “\n” ) ; • i=i+1; • } • while (i<=25); 1 3 4 2
N Y 3 4 2 4 3 1 1 4 3 2 1 2 N N Y Y [1]do{[3][4]} while([2]); [1]while([2]){[3][4]} for([1];[2];[4]){ [3] }
for(…) {…} • int n; • scanf(“%d”,&n); • for ( int i=1;i<=12;i=i+1) • printf( “%d x %d = %d\n”, n, i, (n*i)) ;
for(…) {…} 2 x 1 = 2 2 x 2 = 4 2 x 3 = 6 2 x 4 = 8 2 x 5 = 10 2 x 6 = 12 2 x 7 = 14 2 x 8 = 16 2 x 9 = 18 2 x 10 = 20 2 x 11 = 22 2 x 12 = 24
for(…) {…} • int n; • scanf(“%d”,&n); • for ( int i=1;i<=12;i=i+1) • printf( “%2d x %2d = %2d\n”, n, i, (n*i)) ;
for(…) {…} n=2 n+2 n+1 n+0 i=1 2 x 1 = 2 2 x 2 = 4 2 x 3 = 6 2 x 4 = 8 2 x 5 = 10 2 x 6 = 12 2 x 7 = 14 2 x 8 = 16 2 x 9 = 18 2 x 10 = 20 2 x 11 = 22 2 x 12 = 24 3 x 1 = 3 3 x 2 = 6 3 x 3 = 9 3 x 4 = 12 3 x 5 = 15 3 x 6 = 18 3 x 7 = 21 3 x 8 = 24 3 x 9 = 27 3 x 10 = 30 3 x 11 = 33 3 x 12 = 36 4 x 1 = 4 4 x 2 = 8 4 x 3 = 12 4 x 4 = 16 4 x 5 = 20 4 x 6 = 24 4 x 7 = 28 4 x 8 = 32 4 x 9 = 36 4 x 10 = 40 4 x 11 = 44 4 x 12 = 48 i=2 i=3 i=12
for(…) { for(…){…} …} • int n; • scanf(“%d”,&n); • for (int i=1;i<=n;i=i+1){ • for (int j=1;j <= i;j=j+1) • printf( “*” ) ; • printf( “\n” ) ; • }
1 23 4 5 6 7 89 10 11 12 13 1415 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25
1 6 7 11 12 13 16 17 18 19 21 22 23 24 25 n=5 (n*0)+1 (n*1)+1 (n*2)+1 (n*3)+1 (n*n) (n*4)+1
1 6 7 11 12 13 16 17 18 19 21 22 23 24 25 n=5, k=0, i=1..5, (n*k)+1 k= i / n (n*k)+1 n=5, k=1, i=6..10 (n*k)+1 n=5, k=2, i=11..15 (n*k)+1 n=5, k=3, i=16..20 (n*k)+1 n=5, k=4, i=21..25
int i,k,n; scanf("%d",&n); k=0; for(i=1;i<=(n*n);i++){ if(i<=(n*k+k)+1) printf("*"); if((i%n)==0){ printf("\n"); k=i/n; } }