Discovering DNA structure
140 likes | 279 Vues
Dive into the fascinating history of DNA discovery and its structural components through an engaging activity. Learn about key scientists like Erwin Chargaff, James Watson, and Rosalind Franklin, who contributed to our understanding of DNA. Use simple materials to build short DNA pieces, observe the molecular trends, and understand the pairing of nucleotides—adenine with thymine and guanine with cytosine. Discover how the iconic double helix shape forms, with sugar and phosphate backbones supporting the structure. Embrace the science of genetics through practical exploration!

Discovering DNA structure
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Discovering DNA structure History activity
Erwin Chargaff • Worked with numbers of chemical molecules • Look at the molecules in your bag • These are VERY short DNA pieces • Count up the number of Each molecule • Do you see a trend? What is it?
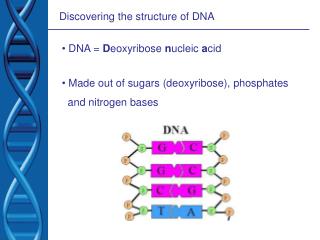
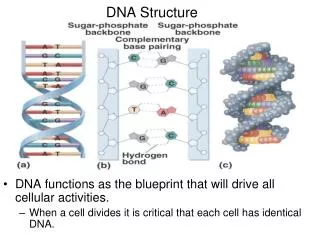
Sugar – deoxyribose • Phosphate – phosphate • A = adenine • T = thymine • G = guanine • C = cytosine
Lord Alexander Todd Structure of nucleotide sugar (deoxyribose) phosphate a base: one of each of A, C, T or G Build as many nucleotides as you can = tape together - have to see letters/words
James Watson and Francis Crick • Used others work to solve structure of DNA
DNA is long and thin and has a repeating structure. • - Rosalind Franklin and Maurice Wilkins
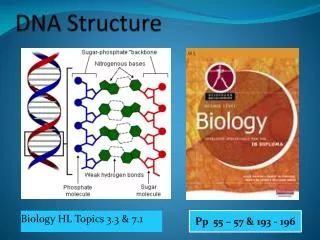
DNA has a backbone made of sugar and phosphate. • - Alexander Todd
DNA is too wide to have just one backbone. • - Rosalind Franklin and Maurice Wilkins
DNA is about [12 cm]* wide. • - Rosalind Franklin • (really, 20 Angstroms)
The backbones of DNA are on the outside of the structure; bases are on the inside. • - Rosalind Franklin
Bases can bond to each other within the same molecule using hydrogen bonds (weak bonds). • - J. M. Gullard and D. O. Jordan
James Watson and Francis Crick • Solved true structure of DNA • Try to fit your nucleotides together – make DNA • So nucleotides match: • Guanine (G) bonds with Cytosine (C) • Thymine (T) bonds with Adenine (A)
DNA structure • Describe it • Do you see how deoxyribose and phosphate chains on outside are opposite? • A-T • G - C
DNA Structure • Shape is called double helix • You made a backbone – it is actually twisted around in a helix shape • Rosalind Franklin discovered “double helix” by doing X-ray diffraction • Can you gently twist your DNA model?