Area of Regular Polygons
50 likes | 449 Vues
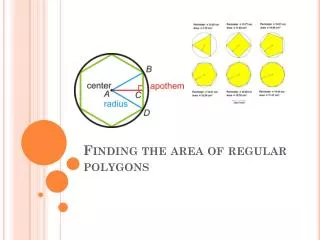
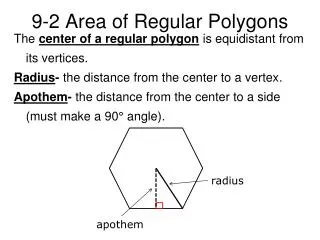
Area of Regular Polygons. A regular polygon has all sides and all angles congruent. You can circumscribe a circle about any regular polygon. The center of the circle is the center of the regular polygon. The radius of a regular polygon is the distance from the center to a vertex.

Area of Regular Polygons
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Area of Regular Polygons • A regular polygon has all sides and all angles congruent. • You can circumscribe a circle about any regular polygon. The center of the circle is the center of the regular polygon. • The radius of a regular polygonis the distance from the center to a vertex. • The apothem of a regular polygon is the perpendicular distance from the center to the sides.
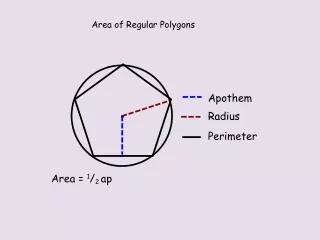
A = Area of Regular Polygons The area of a regular polygon is half the product of the perimeter (p) and the apothem (a).
12.3” 8” Example 1 Find the area of a regular decathon with a 12.3 inch apothem and 8 inch sides. A = ½ ap p = 10(8) = 80” A = (½) (12.3) (80) = 492 sq. in.
10 cm long keg cm = a Example 2 Find the area of a regular hexagon with 10cm sides. The radii of a regular hexagon form 60 angles at the center. We can use the 30-60-90 triangle to find the apothem: short leg = 5 cm p = 6(s) = 60 cm