Transposon
260 likes | 361 Vues
Explore the world of transposons, also known as "jumping genes," that can relocate within DNA sequences, impacting gene expression and regulation. Learn about the mechanisms of transposition, including direct repeats and composite structures, and how transposons regulate metabolic pathways and operons. Delve into negative and positive gene regulation processes, such as the trp and lac operons, and understand the roles of transcription factors in gene expression. Discover practical applications like DNA testing and human gene therapy, as well as safety and ethical considerations related to genetic research.

Transposon
E N D
Presentation Transcript
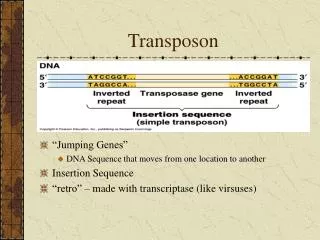
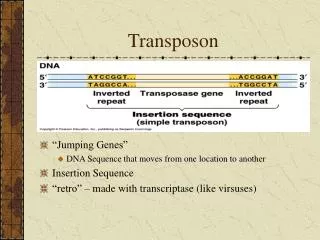
Transposon • “Jumping Genes” • DNA Sequence that moves from one location to another • Insertion Sequence • “retro” – made with transcriptase (like virsuses)
Transposon • Direct repeats
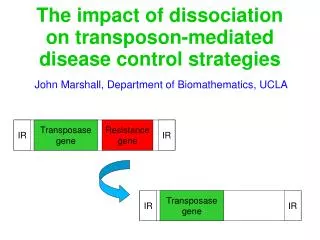
Composite • Adds extra genes between two insertions
Regulation of Metabolic Pathway • Regulate genes • Regulates enzymes
Operons • A unit of genetic material that functions in bacteria and phages • Clustered gene with one promoter • On/off switch
Negative Gene Regulation • Repressible operons • Transcription is inhibited • Inducible operons • Transcription is stimulated
The trp Operon • Corepressor – absent makes tryptophan
Repressor • Corepressor – present stops tryptophan production • Corepressor – helper for repressor
lac operon • Lactose absent / repressor active – operon off
lac operon • Lactose present / repressor inactive – operon on • inducer
Positive Gene Regulation • cAMP • Accumulates when glucose is scarce
Nucleosome • DNA and histone proteins together
Gene Amplification • Not passed to children • Embryos – ribosome production • Cancer cells – drug resistance
Questions??? • Gene loss?? • Gene rearrangement?? • Genome??
Transcription Factors • A protein that binds to DNA and allows for RNA polymerase to attach and begin transcription • Enhancers – bends DNA to allow the factors to be closer to the promoter region
RNA Splicing • Allows alternative mRNA molecules to be built – ex. exons will act as introns
Proteasome • A giant protein complex that destroys proteins tagged for elimination by ubiquitin.
DNA Testing • PCR • RFLP
Practical Application • Diagnosis of Diseases • Human Gene Therapy • DNA Fingerprinting • Environmental Uses • Agricultural Uses
Safety and Ethical Questions • Pages 407-408 or 399